Page 592 - TNFlipTest
P. 592
H52 Hematology
Blood Products and Transfusions Toronto Notes 2019 Tumour Lysis Syndrome
Definition
• groupofmetaboliccomplicationsthatresultfromspontaneousortreatment-relatedbreakdownof cancer cells
• morecommonindiseaseswithlargetumourburdenandhighproliferativerate(highgradelymphoma, leukemia)
Clinical Features
• metabolicabnormalities
■ cells lyse, releasing K+, uric acid, PO43- (increased levels) ■ PO43- binds Ca2+ (decreased Ca2+)
• complications
■ lethal cardiac arrhythmia (increased K+)
■ acute kidney injury (formerly known as renal failure) see Nephrology, NP19
Treatment
• prevention
■ aggressiveIVhydration
■ alkalinization not recommended due to risk of calcium phosphate or xanthine precipitation in renal
tubules
■ allopurinol or rasburicase
■ correction of pre-existing metabolic abnormalities
• dialysis
Blood Products and Transfusions
Blood Products
• RBCs,plateletsandcoagulationfactors(frozenplasma[FP],cryoprecipitate,factorconcentrates)are available for transfusion
• donated blood (1 U = 450-500 mL) is fractionated into these various components ■ centrifugation separates whole blood into RBCs and platelet-rich plasma
■ platelet-rich plasma is further fractionated into platelets and plasma
◆ need to pool together multiple units to obtain therapeutic amounts
◆ FP (previously known as FFP) is plasma frozen within 24 h of collection
◆ cryoprecipitate is the high MW precipitate generated when FP is thawed at low temperatures
Specialized Products
• irradiatedbloodproducts
■ prevent proliferation of donor T-cells in potential or actual bone marrow transplant recipients ■ used for immunocompromised patients or for patients on purine analogue chemotherapy, first-
degree relatives, HLA-matched products and intrauterine transfusions, Hodgkin lymphoma • CMV-negativebloodproducts
■ potential transplant recipients ■ neonates
■ AIDS patients
■ seronegative pregnant women
Red Blood Cells
Packed Red Blood Cells
• storedat4oC
• transfusewithin42dofcollection,otherwisecelllysismayresultinhyperkalemia • infuseeachunitover2h(maxof4h)
Indications for Packed RBC Transfusion
• Hb<70g/L;thismaychangeasperpatient’stoleranceorsymptoms ■ maintain Hb between 70 and 100 g/L during active bleeds
• considermaintainingahigherHbforpatientswith: ■ CAD/unstable coronary syndromes
■ uncontrolled, unpredictable bleeding
■ impairedpulmonaryfunction
■ increased O2 consumption
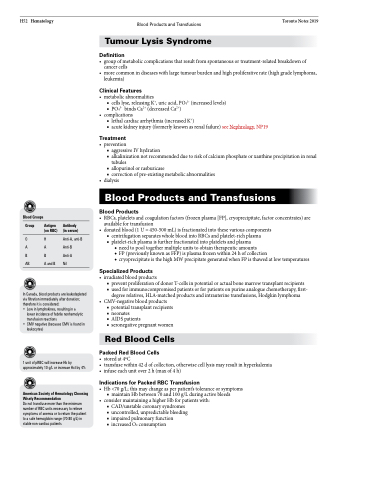
Blood Groups
Group Antigen (on RBC)
O H
A A
B B
AB AandB
Antibody (in serum)
Anti-A, anti-B Anti-B
Anti-A
Nil
In Canada, blood products are leukodepleted via filtration immediately after donation; therefore it is considered:
• Low in lymphokines, resulting in a
lower incidence of febrile nonhemolytic
transfusion reactions
• CMV negative (because CMV is found in
leukocytes)
1 unit of pRBC will increase Hb by approximately 10 g/L or increase Hct by 4%
American Society of Hematology Choosing Wisely Recommendation
Do not transfuse more than the minimum number of RBC units necessary to relieve symptoms of anemia or to return the patient toasafehemoglobinrange(70-80g/L)in stable non-cardiac patients