Page 643 - TNFlipTest
P. 643
Toronto Notes 2019 Travel Medicine
• exposurehistory
■ street foods, untreated water: increased risk of traveller’s diarrhea, enteric fever ■ uncooked meat/unpasteurized dairy: increased risk of parasitic infection
■ body fluids (sexual contacts, tattoos, piercings, IVDU, other injections)
■ increased risk of HBV, HCV, HIV, GC, C. trachomatis, syphilis
■ animal/insect bites: increased risk of malaria, dengue, rickettsioses, rabies
• feverpattern
• incubationperiod:usetheearliestandlatestpossibledatesofexposuretonarrowthedifferential
diagnosis and exclude serious infections
■ <21 d: consider malaria, typhoid fever, dengue fever, chikunguny, rickettsioses; exclude HBV, TB
■ >21 d: consider malaria, TB, typhoid fever; exclude dengue fever, chikungunya, traveller’s diarrhea,
rickettsioses
• bodysystemsaffected:GI,respiratory,CNS,skin
Investigations
• alltravellerswithfevershouldundergothefollowingtests
■ blood work: CBC and differential, liver enzymes, electrolytes, creatinine, thick and thin blood
Infectious Diseases ID43
smears x3 (for malaria), blood C&S
■ urine: urinalysis, urine C&S if dysuria or other localizing signs
• specialtestsbasedonsymptoms,exposurehistory,andgeography ■ stool: C&S, O&P
■ CXR
■ dengue serology for IgM
Fever in traveller from malaria endemic area is malaria until proven otherwise
Pregnancy and Zika Virus
For women and men who have been diagnosed with Zika virus or who have symptoms of Zika including fever, rash, joint pain or red eyes after possible exposure to Zika virus, CDC recommends:
• Women wait at least 8 wk after their symptoms first appeared before trying to get pregnant
• Men wait at least 6 mo after their symptoms first appeared to have unprotected sex
• For men and women without symptoms of Zika virus but who had possible exposure to Zika from recent travel or sexual contact, CDC recommends healthcare providers advise their patients wait at least 8 wk after their possible exposure before trying to get pregnant in order to minimize risk
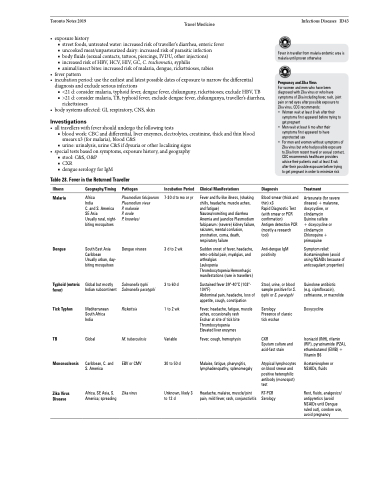
Table 28. Fever in the Returned Traveller
Illness
Malaria
Dengue
Typhoid (enteric fever)
Tick Typhus
TB
Mononucleosis
Zika Virus Disease
Geography/Timing
Africa
India
C. and S. America SE Asia
Usually rural, night- biting mosquitoes
South East Asia Caribbean
Usually urban, day- biting mosquitoes
Global but mostly Indian subcontinent
Mediterranean South Africa India
Global
Caribbean, C. and S. America
Africa, SE Asia, S. America; spreading
Pathogen
Plasmodium falciparum Plasmodium vivax
P. malaraie
P. ovale
P. knowlesi
Dengue viruses
Salmonella typhi Salmonella paratyphi
Rickettsia
M. tuberculosis
EBV or CMV
Zika virus
Incubation Period
7-30 d to mo or yr
3 d to 2 wk
3 to 60 d
1 to 2 wk
Variable
30 to 50 d
Unknown, likely 3 to 12 d
Clinical Manifestations
Fever and flu-like illness, (shaking chills, headache, muscle aches, and fatigue)
Nausea/vomiting and diarrhea Anemia and jaundice Plasmodium falciparum: (severe) kidney failure, seizures, mental confusion, prostration, coma, death, respiratory failure
Sudden onset of fever, headache, retro-orbital pain, myalgias, and arthralgias
Leukopenia
Thrombocytopenia Hemorrhagic manifestations (rare in travellers)
Sustained fever 39°-40°C (103°- 104°F)
Abdominal pain, headache, loss of appetite, cough, constipation
Fever, headache, fatigue, muscle aches, occasionally rash
Eschar at site of tick bite Thrombocytopenia
Elevated liver enzymes Fever, cough, hemoptysis
Malaise, fatigue, pharyngitis, lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly
Headache, malaise, muscle/joint pain, mild fever, rash, conjunctivitis
Diagnosis
Blood smear (thick and thin) x3
Rapid Diagnostic Test (with smear or PCR confirmation)
Antigen detection PCR (mostly a research tool)
Anti-dengue IgM positivity
Stool, urine, or blood sample positive for S. typhi or S. paratyphi
Serology
Presence of classic tick eschar
CXR
Sputum culture and acid-fast stain
Atypical lymphocytes on blood smear and positive heterophilic antibody (monospot) test
RT-PCR Serology
Treatment
Artesunate (for severe disease) + malarone, doxycycline, or clindamycin
Quinine sulfate + doxycycline or clindamycin Chloroquine + primaquine
Symptom relief: Acetaminophen (avoid using NSAIDs because of anticoagulant properties)
Quinolone antibiotic (e.g. ciprofloxacin), ceftriaxone, or macrolide
Doxycycline
Isoniazid (INH), rifamin (RIF), pyrazinamide (PZA), ethambutamol (EMB) + Vitamin B6
Acetaminophen or NSAIDs, fluids
Rest, fluids, analgesics/ antipyretics (avoid NSAIDs until Dengue ruled out), condom use, avoid pregnancy