Page 665 - TNFlipTest
P. 665
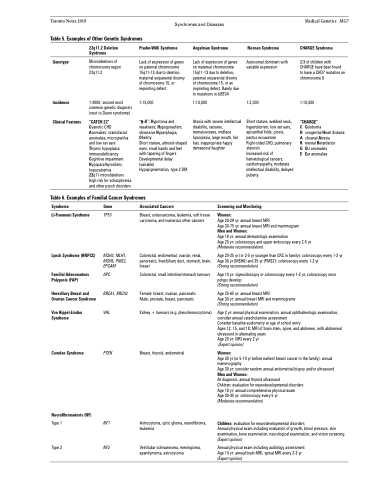
Toronto Notes 2019 Syndromes and Diseases Table 5. Examples of Other Genetic Syndromes
Medical Genetics MG7
CHARGE Syndrome
2/3 of children with CHARGE have been found to have a CHD7 mutation on chromosome 8
1:10,000
“CHARGE”
C Coloboma
H congenital Heart disease A choanal Atresia
R mental Retardation
G GU anomalies
E Ear anomalies
Genotype
Incidence Clinical Features
22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome
Microdeletions of chromosome region 22q11.2
1:4000; second most common genetic diagnosis (next to Down syndrome)
“CATCH 22”
Cyanotic CHD
Anomalies: craniofacial anomalies, micrognathia and low set ears
Thymic hypoplasia: immunodeficiency Cognitive impairment Hypoparathyroidism, hypocalcemia
22q11 microdeletions High risk for schizophrenia and other psych disorders
Prader-Willi Syndrome
Lack of expression of genes on paternal chromosome 15q11-13 due to deletion, maternal uniparental disomy of chromosome 15, or imprinting defect
1:15,000
“H3O”: Hypotonia and
weakness, Hypogonadism, obsessive Hyperphagia, Obesity
Short stature, almond-shaped eyes, small hands and feet with tapering of fingers Developmental delay (variable)
Hypopigmentation, type 2 DM
Angelman Syndrome
Lack of expression of genes on maternal chromosome 15q11-13 due to deletion, paternal uniparental disomy of chromosome 15, or an imprinting defect. Rarely due to mutations in UBE3A
1:10,000
Ataxia with severe intellectual disability, seizures, tremulousness, midface hypoplasia, large mouth, fair hair, inappropriate happy demeanour/laughter
Noonan Syndrome
Autosomal dominant with variable expression
1:2,000
Short stature, webbed neck, hypertelorism, low set ears, epicanthal folds, ptosis, pectus excavatum Right-sided CHD, pulmonary stenosis
Increased risk of hematological cancers, cardiomyopathy, moderate intellectual disability, delayed puberty
Table 6. Examples of Familial Cancer Syndromes
Syndrome
Li-Fraumeni Syndrome
Lynch Syndrome (HNPCC)
Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP)
Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer Syndrome
Von Hippel-Lindau Syndrome
Cowden Syndrome
Neurofibromatosis (NF)
Type 1
Type 2
Gene
TP53
MSH2, MLH1, MSH6, PMS2, EPCAM
APC
BRCA1, BRCA2 VHL
PTEN
NF1
NF2
Associated Cancers
Breast, osteosarcoma, leukemia, soft tissue carcinoma, and numerous other cancers
Colorectal, endometrial, ovarian, renal, pancreatic, liver/biliary duct, stomach, brain, breast
Colorectal, small intestine/stomach tumours
Female: breast, ovarian, pancreatic Male: prostate, breast, pancreatic
Kidney + tumours (e.g. pheochromocytoma)
Breast, thyroid, endometrial
Astrocytoma, optic glioma, neurofibroma, leukemia
Vestibular schwannoma, meningioma, ependymoma, astrocytoma
Screening and Monitoring
Women:
Age 20-29 yr: annual breast MRI
Age 30-75 yr: annual breast MRI and mammogram
Men and Women:
Age 18 yr: annual dermatologic examination
Age 25 yr: colonoscopy and upper endoscopy every 2-5 yr (Moderate recommendation)
Age 20-25 yr (or 2-5 yr younger than CRC in family): colonoscopy every 1-2 yr Age 30 yr (MSH6) and 35 yr (PMS2): colonoscopy every 1-2 yr
(Strong recommendation)
Age 10 yr: sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy every 1-2 yr, colonoscopy once polyps develop
(Strong recommendation)
Age 25-65 yr: annual breast MRI
Age 30 yr: annual breast MRI and mammograms (Strong recommendation)
Age 2 yr: annual physical examination, annual ophthalmologic examination, consider annual catecholamine assessment
Consider baseline audiometry at age of school entry
Ages 12, 15, and 18: MRI of brain stem, spine, and abdomen, with abdominal ultrasound in alternating years
Age 20 yr: MRI every 2 yr
(Expert opinion)
Women:
Age 30 yr (or 5-10 yr before earliest breast cancer in the family): annual mammography
Age 30 yr: consider random annual endometrial biopsy and/or ultrasound Men and Women:
At diagnosis: annual thyroid ultrasound
Children: evaluation for neurodevelopmental disorders Age 18 yr: annual comprehensive physical exam
Age 30-35 yr: colonoscopy every 5 yr
(Moderate recommendation)
Children: evaluation for neurodevelopmental disorders
Annual physical exam including evaluation of growth, blood pressure, skin examination, bone examination, neurological examination, and vision screening (Expert opinion)
Annual physical exam including audiology assessment Age 10 yr: annual brain MRI, spinal MRI every 2-3 yr (Expert opinion)