Page 67 - TNFlipTest
P. 67
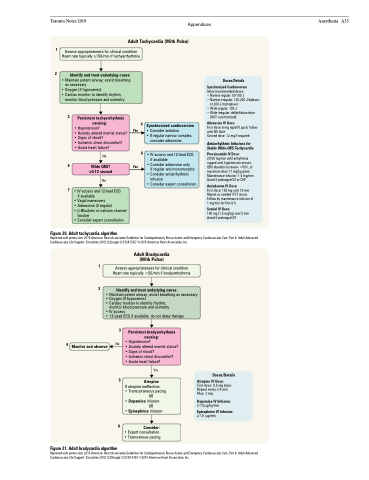
Toronto Notes 2019 Appendices Adult Tachycardia (With Pulse)
1
2
Anesthesia A33
Assess appropriateness for clinical condition Heart rate typically ≥150/min if tachyarrhythmia
Identify and treat underlying cause
• Maintain patent airway; assist breathing as necessary
• Oxygen (if hypoxemic)
• Cardiac monitor to identify rhythm;
monitor blood pressure and oximetry
3 Persistent tachyarrhythmia causing:
4 Synchronized cardioversion
• Consider sedation
• If regular narrow complex,
consider adenosine
IV access and 12-lead ECG if available
Consider adenosine only
if regular and monomorphic Consider antiarrhythmic infusion
Consider expert consultation
Doses/Details
Synchronized Cardioversion
Initial recommended doses: • Narrow regular: 50-100 J
• Narrow irregular: 120-200 J biphasic
or 200 J monophasic
• Wide regular: 100 J
• Wide irregular: defibrillation dose
(NOT synchronized)
Adenosine IV Dose:
First dose: 6 mg rapid IV push; follow with NS flush
Second dose: 12 mg if required
Antiarrhythmic Infusions for Stable Wide-QRS Tachycardia
Procainamide IV Dose:
20-50 mg/min until arrhythmia suppressed, hypotension ensues, QRS duration increases >50%, or maximum dose 17 mg/kg given Maintenance infusion: 1-4 mg/min Avoid if prolonged QT or CHF
Amiodarone IV Dose:
First dose: 150 mg over 10 min Repeat as needed if VT recurs Follow by maintenance infusion of 1 mg/min for first 6 h
Sotalol IV Dose:
100 mg (1.5 mg/kg) over 5 min Avoid if prolonged QT
5
Wide QRS? ≥0.12 second
No
Yes
• • •
• Hypotension?
• Acutely altered mental status? • Signs of shock?
• Ischemic chest discomfort?
• Acute heart failure?
Yes
No 6•
7 • IV access and 12-lead ECG if available
• Vagal maneuvers
• Adenosine (if regular)
• β-Blockers or calcium channel
blocker
• Consider expert consultation
Figure 20. Adult tachycardia algorithm
Reprinted with permission: 2015 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care, Part 8: Adult Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support. Circulation 2010;122(suppl 3):S729-S767 ©2015 American Heart Association, Inc.
1
2
Assess appropriateness for clinical condition Heart rate typically <50/min if bradyarrhythmia
Adult Bradycardia (With Pulse)
Identify and treat underlying cause
• Maintain patent airway; assist breathing as necessary
• Oxygen (if hypoxemic)
• Cardiac monitor to identify rhythm;
monitor blood pressure and oximetry
• IV access
• 12-Lead ECG if available; do not delay therapy
3
4 No Monitor and observe
Persistent bradyarrhythmia causing:
• Hypotension?
• Acutely altered mental status? • Signs of shock?
• Ischemic chest discomfort?
• Acute heart failure?
Figure 21. Adult bradycardia algorithm
5
6
Yes
Atropine
Doses/Details
Atropine IV Dose:
First dose: 0.5 mg bolus Repeat every 3-5 min Max: 3 mg
Dopamine IV Infusion:
2-10 μg/kg/min Epinephrine IV Infusion:
2-10 μg/min
If atropine ineffective:
• Transcutaneous pacing
OR
• Dopamine infusion
OR
• Epinephrine infusion
Consider:
• Expert consultation • Transvenous pacing
Reprinted with permission: 2015 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care, Part 8: Adult Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support. Circulation 2010;1229(suppl 3):S729-S767 ©2015 American Heart Association, Inc.