Page 722 - TNFlipTest
P. 722
NP22 Nephrology
Parenchymal Kidney Diseases Toronto Notes 2019
◆ hereditary nephritis (Alport Syndrome – Type IV collagen mutation): X-linked nephritis often associated with sensorineural hearing loss; proteinuria <2 g/d
◆ thin basement membrane disease: usually autosomal dominant, without proteinuria; benign
◆ benign recurrent hematuria: hematuria associated with febrile illness, exercise, or immunization;
a diagnosis of exclusion after other possibilities are ruled out
2 . NEPHRITIC SYNDROME
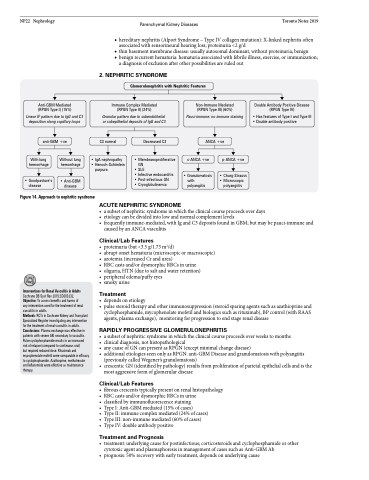
Glomerulonephritis with Nephritic Features
Anti-GBM Mediated (RPGN Type I) (15%)
Linear IF pattern due to IgG and C3 deposition along capillary loops
anti-GBM +ve
Immune Complex Mediated (RPGN Type II) (24%)
Granular pattern due to subendothelial or subepithelial deposits of IgG and C3
Non-Immune Mediated (RPGN Type III) (60%)
Pauci-immune: no immune staining
ANCA +ve
Double Antibody Positive Disease (RPGN Type IV)
• Has features of Type I and Type III • Double antibody positive
C3 normal
Decreased C3
With lung hemorrhage
• Goodpasture’s disease
Without lung hemorrhage
• Anti-GBM disease
• Membranoproliferative • Henoch-Schönlein GN
• SLE
• Infective endocarditis • Post-infectious GN
• Cryoglobulinemia
ACUTE NEPHRITIC SYNDROME
c-ANCA +ve
• Granulomatosis with
polyangiitis
p-ANCA +ve
• Churg-Strauss • Microscopic
polyangiitis
• IgA nephropathy purpura
Figure 14. Approach to nephritic syndrome
Interventions for Renal Vasculitis in Adults
Cochrane DB Syst Rev 2015;CD003232.
Objective: To assess benefits and harms of
any intervention used for the treatment of renal vasculitis in adults.
Methods: RCTs in Cochrane Kidney and Transplant Specialized Register investigating any intervention for the treatment of renal vasculitis in adults. Conclusions: Plasma exchange was effective in patients with severe AKI secondary to vasculitis. Pulse cyclophosphamide results in an increased risk of relapse (compared to continuous oral)
but required reduced dose. Rituximab and mycophenolate mofetil were comparable in efficacy to cyclophophamide. Azathioprine, methotrexate and leflunomide were effective as maintenance therapy.
• asubsetofnephriticsyndromeinwhichtheclinicalcourseproceedsoverdays
• etiologycanbedividedintolowandnormalcomplementlevels
• frequentlyimmune-mediated,withIgandC3depositsfoundinGBM;butmaybepauci-immuneand
caused by an ANCA vasculitis
Clinical/Lab Features
• proteinuria(but<3.5g/1.73m2/d)
• abruptonsethematuria(microscopicormacroscopic) • azotemia(increasedCrandurea)
• RBCcastsand/ordysmorphicRBCsinurine
• oliguria,HTN(duetosaltandwaterretention)
• peripheraledema/puffyeyes
• smokyurine
Treatment
• dependsonetiology
• pulsesteroidtherapyandotherimmunosuppression(steroidsparingagentssuchasazathioprineand
cyclophosphamide, mycophenolate mofetil and biologics such as rituximab), BP control (with RAAS agents, plasma exchange), monitoring for progression to end stage renal disease
RAPIDLY PROGRESSIVE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
• asubsetofnephriticsyndromeinwhichtheclinicalcourseproceedsoverweekstomonths
• clinicaldiagnosis,nothistopathological
• anycauseofGNcanpresentasRPGN(exceptminimalchangedisease)
• additionaletiologiesseenonlyasRPGN:anti-GBMDiseaseandgranulomatosiswithpolyangiitis
(previously called Wegener’s granulomatosis)
• crescenticGN(identifiedbypathology)resultsfromproliferationofparietalepithelialcellsandisthe
most aggressive form of glomerular disease
Clinical/Lab Features
• fibrouscrescentstypicallypresentonrenalhistopathology • RBCcastsand/ordysmorphicRBCsinurine
• classifiedbyimmunofluorescencestaining
• TypeI:Anti-GBMmediated(15%ofcases)
• TypeII:immunecomplexmediated(24%ofcases) • TypeIII:non-immunemediated(60%ofcases)
• TypeIV:doubleantibodypositive
Treatment and Prognosis
• treatment:underlyingcauseforpostinfectious;corticosteroidsandcyclophosphamideorother cytotoxic agent and plasmaphoresis in management of cases such as Anti-GBM Ab
• prognosis:50%recoverywithearlytreatment,dependsonunderlyingcause