Page 82 - TNFlipTest
P. 82
C14 Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery
Approach to ECGs Toronto Notes 2019 Cardiac Catheterization and Angiography
Right Heart Catheterization (Swan-Ganz Catheter)
• description:alsoknownaspulmonaryarterycatheterization
■ obtain direct measurements of central venous, right-sided intracardiac, pulmonary artery, and
pulmonary artery occlusion pressures
■ can estimate cardiac output, systemic and pulmonary vascular resistance as well as mixed venous
oxyhemoglobin saturation, oxygen delivery, and oxygen uptake
■ right atrial, right ventricular, and pulmonary artery pressures are recorded
■ can also be used to measure the Cardiac Index (CI)
◆ CI = CO/body surface area
◆ cardiac index is a measure of cardiac function
◆ <1.8 L/min/m2 usually means cardiogenic shock ◆ 2.6-4.2 L/min/m2 is considered normal
■ pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP)
◆ obtained by advancing the catheter to wedge in the distal pulmonary artery ◆ records pressure measured from the pulmonary venous system
◆ in the absence of pulmonary venous disease reflects left atrial pressure
• indications
■ unexplained or unknown volume status in shock
■ severe cardiogenic shock (e.g. acute valvular disease, suspected pericardial tamponade)
■ suspected or known pulmonary artery hypertension
■ severe underlying cardiopulmonary disease (e.g. congenital heart disease, left-to-right shunt, severe
valvular disease, pulmonary hypertension) and undergoing corrective or other surgery • contraindications
■ lack of consent
■ infection at the insertion site
■ the presence of a right ventricular assist device ■ insertion during cardiopulmonary bypass
• risks
■ complications for diagnostic catheterization <1%
■ inadequate diagnostic procedures occur in <1% of cases
■ complications of insertion: atrial and/or ventricular arrhythmias (~3% of patients)
■ catheter misplacement or knotting (uncommon)
■ perforation of a cardiac chamber and rupture of a cardiac valve or the pulmonary artery (rare)
■ complications of catheterization: pulmonary artery rupture, pulmonary infarction, thromboembolic
events, infection, and data misinterpretation
■ within 24 h of catheterization: death, MI, or stroke (0.2% to 0.3% of patients)
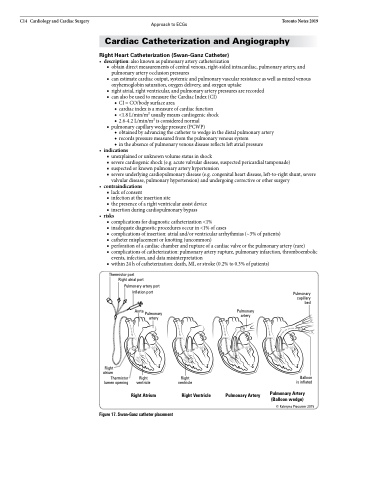
Thermistor port Right atrial port
Right atrium
Thermistor lumen opening
Right ventricle
Right Ventricle
Pulmonary artery port Inflation port
Aorta Pulmonary artery
Right ventricle
Pulmonary artery
Pulmonary capillary bed
Balloon is inflated
Pulmonary Artery (Balloon wedge)
© Kateryna Procunier 2015
Right Atrium
Figure 17. Swan-Ganz catheter placement
Pulmonary Artery