Page 89 - TNFlipTest
P. 89
Toronto Notes 2019 Arrhythmias
– LV dysfunction: amiodarone
– CAD: β-blockers, amiodarone
– if antiarrhythmic drugs fail or are not tolerated, can consider RF ablation for rhythm/ symptom
control
6 . AV NODAL RE-ENTRANT TACHYCARDIA (AVNRT)
• re-entrantcircuitusingdualpathways(fastconductingβ-fibresandslowconductingα-fibres)within or near the AV node; often found in the absence of structural heart disease – cause is commonly idiopathic, although familial AVNRT has been reported
• suddenonsetandoffset
• fastregularrhythm:rate150-250bpm
• usuallyinitiatedbyasupraventricularorventricularprematurebeat
• AVNRTaccountsfor60-70%ofallparoxysmalSVTs
• retrogradePwavesmaybeseenbutareusuallylostintheQRScomplex
• treatment
■ acute: Valsalva maneuver or carotid sinus pressure technique, adenosine is first choice if unresponsive to vagal maneuvers; if no response, try metoprolol, digoxin, diltiazem, electrical cardioversion if patient hemodynamically unstable (hypotension, angina, or CHF)
■ long-term: 1st line – β-blocker, diltiazem, digoxin; 2nd line – flecainide, propafenone; 3rd line – catheter ablation
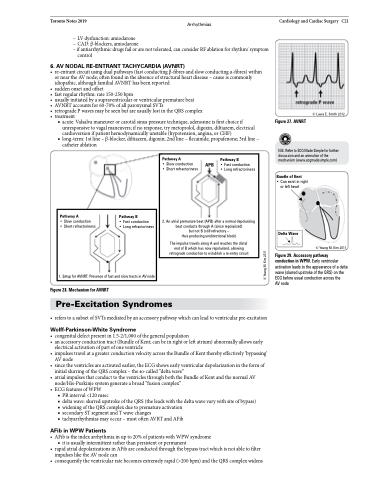
Figure 28. Mechanism for AVNRT
Pre-Excitation Syndromes
• referstoasubsetofSVTsmediatedbyanaccessorypathwaywhichcanleadtoventricularpre-excitation
Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome
• congenitaldefectpresentin1.5-2/1,000ofthegeneralpopulation
• anaccessoryconductiontract(BundleofKent;canbeinrightorleftatrium)abnormallyallowsearly
electrical activation of part of one ventricle
• impulsestravelatagreaterconductionvelocityacrosstheBundleofKenttherebyeffectively‘bypassing’
AV node
• sincetheventriclesareactivatedearlier,theECGshowsearlyventriculardepolarizationintheformof
initial slurring of the QRS complex – the so-called “delta wave”
• atrialimpulsesthatconducttotheventriclesthroughboththeBundleofKentandthenormalAV
node/His-Purkinje system generate a broad “fusion complex”
• ECGfeaturesofWPW
■ PR interval <120 msec
■ delta wave: slurred upstroke of the QRS (the leads with the delta wave vary with site of bypass) ■ widening of the QRS complex due to premature activation
■ secondary ST segment and T wave changes
■ tachyarrhythmias may occur – most often AVRT and AFib
AFib in WPW Patients
• AFibistheindexarrhythmiainupto20%ofpatientswithWPWsyndrome ■ it is usually intermittent rather than persistent or permanent
• rapidatrialdepolarizationsinAFibareconductedthroughthebypasstractwhichisnotabletofilter impulses like the AV node can
• consequentlytheventricularratebecomesextremelyrapid(>200bpm)andtheQRScomplexwidens
Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery C21
Figure 27. AVNRT
© Laura E. Smith 2012
N.B. Refer to ECG Made Simple for further discussion and an animation of the mechanism (www.ecgmadesimple.com)
Pathway A
• Slow conduction APB • Short refractoriness
Pathway B
• Fast conduction
• Long refractoriness
2. An atrial premature beat (APB) after a normal depolarizing beat conducts through A (since repolarized)
but not B (still refractory –
thus producing unidirectional block)
The impulse travels along A and reaches the distal end of B which has now repolarized, allowing retrograde conduction to establish a re-entry circuit
Bundle of Kent
• Can exist in right or left heart
Pathway A
• Slow conduction
• Short refractoriness
Pathway B
• Fast conduction
• Long refractoriness
1. Setup for AVNRT: Presence of fast and slow tracts in AV node
Delta Wave
Figure 29. Accessory pathway conduction in WPW. Early ventricular activation leads to the appearance of a delta wave (slurred upstroke of the QRS) on the ECG before usual conduction across the
AV node
© Young M. Kim 2011
© Young M. Kim 2011