Page 995 - TNFlipTest
P. 995
Toronto Notes 2019
Hearing
Otolaryngology OT9
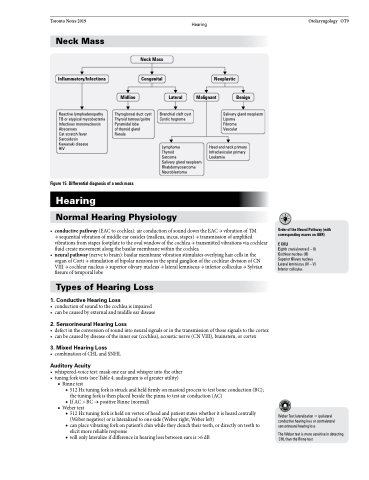
Neck Mass
Inflammatory/Infections
Reactive lymphadenopathy TB or atypical mycobacteria Infectious mononucleosis Abscesses
Cat scratch fever Sarcoidosis Kawasaki disease HIV
Neck Mass
Congenital
Neoplastic
Midline
Thyroglossal duct cyst Thyroid tumour/goitre Pyramidal lobe
of thyroid gland Ranula
Lateral
Branchial cleft cyst Cystic hygroma
Lymphoma
Thyroid
Sarcoma
Salivary gland neoplasm Rhabdomyosarcoma Neuroblastoma
Malignant
Benign
Salivary gland neoplasm Lipoma
Fibroma
Vascular
Head and neck primary Infraclavicular primary Leukemia
Figure 15. Differential diagnosis of a neck mass
Hearing
Normal Hearing Physiology
• conductivepathway(EACtocochlea):airconductionofsounddowntheEAC→vibrationofTM
→ sequential vibration of middle ear ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes) → transmission of amplified vibrations from stapes footplate to the oval window of the cochlea → transmitted vibrations via cochlear fluid create movement along the basilar membrane within the cochlea
• neural pathway (nerve to brain): basilar membrane vibration stimulates overlying hair cells in the organ of Corti → stimulation of bipolar neurons in the spiral ganglion of the cochlear division of CN VIII → cochlear nucleus → superior olivary nucleus → lateral lemniscus → inferior colliculus → Sylvian fissure of temporal lobe
Types of Hearing Loss
1 . Conductive Hearing Loss
• conductionofsoundtothecochleaisimpaired
• canbecausedbyexternalandmiddleeardisease
2 . Sensorineural Hearing Loss
• defectintheconversionofsoundintoneuralsignalsorinthetransmissionofthosesignalstothecortex • canbecausedbydiseaseoftheinnerear(cochlea),acousticnerve(CNVIII),brainstem,orcortex
3 . Mixed Hearing Loss
• combinationofCHLandSNHL
Auditory Acuity
• whispered-voicetest:maskoneearandwhisperintotheother • tuningforktests(seeTable4;audiogramisofgreaterutility)
■ Rinne test
◆ 512 Hz tuning fork is struck and held firmly on mastoid process to test bone conduction (BC);
the tuning fork is then placed beside the pinna to test air conduction (AC) ◆ If AC > BC → positive Rinne (normal)
■ Weber test
◆ 512 Hz tuning fork is held on vertex of head and patient states whether it is heard centrally
(Weber negative) or is lateralized to one side (Weber right, Weber left)
◆ can place vibrating fork on patient’s chin while they clench their teeth, or directly on teeth to
elicit more reliable response
◆ will only lateralize if difference in hearing loss between ears is >6 dB
Order of the Neural Pathway (with corresponding waves on ABR)
E COLI
Eighth cranial nerve (I – II) Cochlear nucleus (III) Superior Olivary nucleus Lateral leminiscus (IV – V) Inferior colliculus
Weber Test lateralization = ipsilateral conductive hearing loss or contralateral sensorineural hearing loss
The Weber test is more sensitive in detecting CHL than the Rinne test