Page 1136 - TNFlipTest
P. 1136
PL14 Plastic Surgery
Wounds Toronto Notes 2019
Random Pattern Flaps
• bloodsupplybydermalandsubdermalplexustoskinandsubdermaltissuewithrandomvascular supply
• limitedlength:widthratiotoensureadequatebloodsupply(typically3:1intheheadandneck,1-2:1 elsewhere)
• flapchoiceisoftenacombinationofavailabletissue,typeoftissueneeded,locationofreconstruction site with respect to donor site, blood supply, ability to close the donor site and surgeon preference
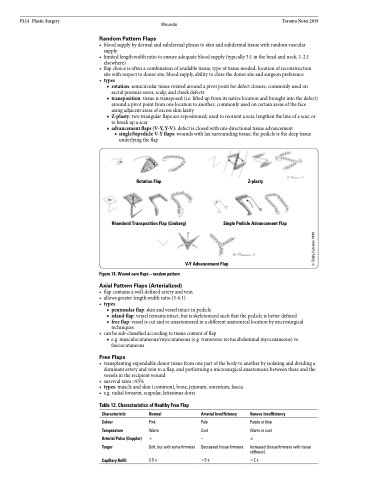
• types
■ rotation:semicirculartissuerotatedaroundapivotpointfordefectclosure;commonlyusedon
sacral pressure sores, scalp, and cheek defects
■ transposition:tissueistransposed(i.e.liftedupfromitsnativelocationandbroughtintothedefect)
around a pivot point from one location to another; commonly used on certain areas of the face
using adjacent areas of excess skin laxity
■ Z-plasty:twotriangularflapsarerepositioned;usedtoreorientascar,lengthenthelineofascar,or
to break up a scar
■ advancement flaps (V-Y, Y-V): defect is closed with uni-directional tissue advancement
◆ single/bipedicle V-Y flaps: wounds with lax surrounding tissue; the pedicle is the deep tissue underlying the flap
Rotation Flap Z-plasty
Rhomboid Transposition Flap (Limberg) Single Pedicle Advancement Flap
Figure 18. Wound care flaps – random pattern
Axial Pattern Flaps (Arterialized)
V-Y Advancement Flap
• flapcontainsawell-definedarteryandvein • allowsgreaterlength:widthratio(5-6:1)
• types
■ peninsularflap:skinandvesselintactinpedicle
■ islandflap:vesselremainsintact,butisskeletonizedsuchthatthepedicleisbetterdefined
■ freeflap:vesseliscutandre-anastomosedinadifferentanatomicallocationbymicrosurgical
techniques
• canbesub-classifiedaccordingtotissuecontentofflap
■ e.g. musculocutaneous/myocutaneous (e.g. transverse rectus abdominal myocutaneous) vs. fasciocutaneous
Free Flaps
• transplantingexpendabledonortissuefromonepartofthebodytoanotherbyisolatinganddividinga dominant artery and vein to a flap, and performing a microsurgical anastomosis between these and the vessels in the recipient wound
• survivalrates>95%
• types:muscleandskin(common),bone,jejunum,omentum,fascia
• e.g.radialforearm,scapular,latissimusdorsi
Table 12. Characteristics of Healthy Free Flap
Characteristic
Colour
Temperature
Arterial Pulse (Doppler) Turgor
Normal
Pink
Warm
+
Soft, but with some firmness
Arterial Insufficiency
Pale
Cool
–
Decreased tissue firmness
Venous Insufficiency
Purple or blue
Warm or cool
±
Increased (tissue firmness with tissue stiffness)
<2 s
Capillary Refill
2-5 s
>5 s
© Teddy Cameron 1999