Page 1144 - TNFlipTest
P. 1144
PL22 Plastic Surgery
Burns Toronto Notes 2019
• earlyexcisionandgraftingisthemainstayoftreatmentfordeep/fullthicknessburns
• initialdressingshoulddecreasebacterialproliferation
• preventionofwoundcontractures:pressuredressings,jointsplints,earlyphysiotherapy
Other Considerations in Burn Management
Vascular Permeability and Edema Immunosuppression
Renal Failure (2o toRenal Blood Flow)
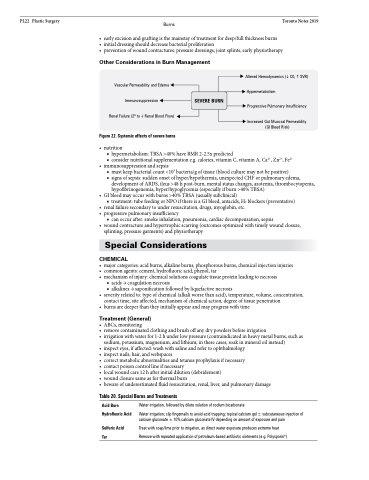
Figure 22. Systemic effects of severe burns
SEVERE BURN
Altered Hemodynamics (CO,SVR) Hypermetabolism
Progressive Pulmonary Insufficiency
Increased Gut Mucosal Permeability (GI Bleed Risk)
• nutrition
■ hypermetabolism: TBSA >40% have BMR 2-2.5x predicted
■ consider nutritional supplementation e.g. calories, vitamin C, vitamin A, Ca2+, Zn2+, Fe2+
• immunosuppressionandsepsis
■ must keep bacterial count <105 bacteria/g of tissue (blood culture may not be positive)
■ signs of sepsis: sudden onset of hyper/hypothermia, unexpected CHF or pulmonary edema,
development of ARDS, ileus >48 h post-burn, mental status changes, azotemia, thrombocytopenia,
hypofibrinogenemia, hyper/hypoglycemia (especially if burn >40% TBSA)
• GIbleedmayoccurwithburns>40%TBSA(usuallysubclinical)
■ treatment: tube feeding or NPO if there is a GI bleed, antacids, H2 blockers (preventative)
• renalfailuresecondarytounderresuscitation,drugs,myoglobin,etc.
• progressivepulmonaryinsufficiency
■ can occur after: smoke inhalation, pneumonia, cardiac decompensation, sepsis
• woundcontractureandhypertrophicscarring(outcomesoptimizedwithtimelywoundclosure,
splinting, pressure garments) and physiotherapy
Special Considerations
CHEMICAL
• majorcategories:acidburns,alkalineburns,phosphorousburns,chemicalinjectioninjuries • commonagents:cement,hydrofluoricacid,phenol,tar
• mechanismofinjury:chemicalsolutionscoagulatetissueproteinleadingtonecrosis
■ acids → coagulation necrosis
■ alkalines → saponification followed by liquefactive necrosis
• severityrelatedto:typeofchemical(alkaliworsethanacid),temperature,volume,concentration,
contact time, site affected, mechanism of chemical action, degree of tissue penetration • burnsaredeeperthantheyinitiallyappearandmayprogresswithtime
Treatment (General)
• ABCs, monitoring
• removecontaminatedclothingandbrushoffanydrypowdersbeforeirrigation
• irrigationwithwaterfor1-2hunderlowpressure(contraindicatedinheavymetalburns,suchas
sodium, potassium, magnesium, and lithium; in these cases, soak in mineral oil instead) • inspecteyes,ifaffected:washwithsalineandrefertoophthalmology
• inspectnails,hair,andwebspaces
• correctmetabolicabnormalitiesandtetanusprophylaxisifnecessary
• contactpoisoncontrollineifnecessary
• localwoundcare12hafterinitialdilution(debridement)
• woundclosuresameasforthermalburn
• bewareofunderestimatedfluidresuscitation,renal,liver,andpulmonarydamage
Table 20. Special Burns and Treatments
Acid Burn Hydrofluoric Acid
Sulfuric Acid Tar
Water irrigation, followed by dilute solution of sodium bicarbonate
Water irrigation; clip fingernails to avoid acid trapping; topical calcium gel ± subcutaneous injection of calcium gluconate ± 10% calcium gluconate IV depending on amount of exposure and pain
Treat with soap/lime prior to irrigation, as direct water exposure produces extreme heat Remove with repeated application of petroleum-based antibiotic ointments (e.g. Polysporin®)