Page 1322 - TNFlipTest
P. 1322
U4 Urology
Urologic History
Toronto Notes 2019
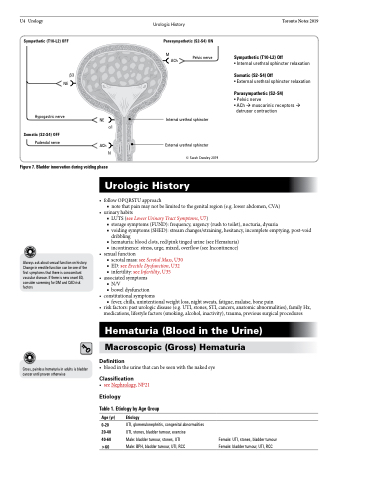
Sympathetic (T10-L2) OFF
β3
Parasympathetic (S2-S4) ON
M
ACh
Pelvic nerve
Sympathetic (T10-L2) Off
• Internal urethral sphincter relaxation
Somatic (S2-S4) Off
• External urethral sphincter relaxation
Parasympathetic (S2-S4)
• Pelvic nerve
• AChmuscarinic receptors
detrusor contraction
NE
Hypogastric nerve
Somatic (S2-S4) OFF
Pudendal nerve
NE
ACh
α1
N
Internal urethral sphincter
External urethral sphincter
© Sarah Crawley 2019
Figure 7. Bladder innervation during voiding phase
Urologic History
Always ask about sexual function on history. Change in erectile function can be one of the first symptoms that there is concomitant vascular disease. If there is new onset ED, consider screening for DM and CAD risk factors
Gross, painless hematuria in adults is bladder cancer until proven otherwise
• followOPQRSTUapproach
■ note that pain may not be limited to the genital region (e.g. lower abdomen, CVA)
• urinaryhabits
■ LUTS (see Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms, U7)
■ storage symptoms (FUND): frequency, urgency (rush to toilet), nocturia, dysuria
■ voiding symptoms (SHED): stream changes/straining, hesitancy, incomplete emptying, post-void
dribbling
■ hematuria: blood clots, red/pink tinged urine (see Hematuria) ■ incontinence: stress, urge, mixed, overflow (see Incontinence)
• sexualfunction
■ scrotal mass: see Scrotal Mass, U30 ■ ED: see Erectile Dysfunction, U32 ■ infertility: see Infertility, U35
• associated symptoms ■ N/V
■ bowel dysfunction
• constitutionalsymptoms
■ fever, chills, unintentional weight loss, night sweats, fatigue, malaise, bone pain
• riskfactors:pasturologicdisease(e.g.UTI,stones,STI,cancers,anatomicabnormalities),familyHx,
medications, lifestyle factors (smoking, alcohol, inactivity), trauma, previous surgical procedures
Hematuria (Blood in the Urine)
Macroscopic (Gross) Hematuria
Definition
• bloodintheurinethatcanbeseenwiththenakedeye
Classification
• seeNephrology,NP21 Etiology
Table 1. Etiology by Age Group
Age (yr)
0-20 20-40 40-60 >60
Etiology
UTI, glomerulonephritis, congenital abnormalities UTI, stones, bladder tumour, exercise
Male: bladder tumour, stones, UTI
Male: BPH, bladder tumour, UTI, RCC
Female: UTI, stones, bladder tumour Female: bladder tumour, UTI, RCC