Page 1324 - TNFlipTest
P. 1324
U6 Urology
Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction
Toronto Notes 2019
Microscopic Hematuria
Definition
• bloodintheurinethatisnotvisibletothenakedeye
• >2RBCs/HPFonurinalysisofatleasttwoseparatesamples
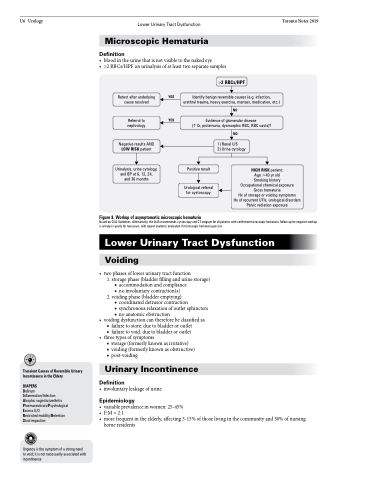
Retest after underlying cause resolved
Referral to nephrology
Negative results AND LOW RISK patient
Urinalysis, urine cytology, and BP at 6, 12, 24, and 36 months
>2 RBCs/HPF
YES Identify benign reversible causes (e.g. infection, urethral trauma, heavy exercise, menses, medication, etc.)
NO
YES Evidence of glomerular disease
(Cr, proteinuria, dysmorphic RBC, RBC casts)? NO
Positive result
Urological referral for cystoscopy
1) Renal U/S
2) Urine cytology
HIGH RISK patient:
Age >40 yr old Smoking history Occupational chemical exposure Gross hematuria
Hx of storage or voiding symptoms Hx of recurrent UTIs, urological disorders Pelvic radiation exposure
Transient Causes of Reversible Urinary Incontinence in the Eldery
DIAPERS
Delirium Inflammation/Infection Atrophic vaginitis/urethritis Pharmaceuticals/Psychological Excess U/O
Restricted mobility/Retention Stool impaction
Urgency is the symptom of a strong need to void; it is not necessarily associated with incontinence
Based on CUA Guidelines. Alternatively, the AUA recommends cystoscopy and CT urogram for all patients with confirmed microscopic hematuria; follow-up for negative workup is urinalysis yearly for two years, with repeat anatomic evaluation if microscopic hematuria persists
Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction
Voiding
• twophasesoflowerurinarytractfunction
1. storage phase (bladder filling and urine storage)
◆ accommodation and compliance
◆ no involuntary contraction(s) 2. voiding phase (bladder emptying)
◆ coordinated detrusor contraction
◆ synchronous relaxation of outlet sphincters ◆ no anatomic obstruction
• voidingdysfunctioncanthereforebeclassifiedas ■ failure to store: due to bladder or outlet
■ failure to void: due to bladder or outlet
• threetypesofsymptoms
■ storage (formerly known as irritative)
■ voiding (formerly known as obstructive) ■ post-voiding
Urinary Incontinence
Definition
• involuntaryleakageofurine
Epidemiology
• variableprevalenceinwomen:25-45%
• F:M=2:1
• morefrequentintheelderly,affecting5-15%ofthoselivinginthecommunityand50%ofnursing
home residents
Figure 8. Workup of asymptomatic microscopic hematuria