Page 245 - TNFlipTest
P. 245
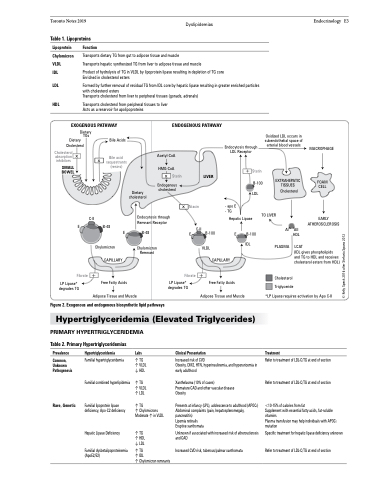
Toronto Notes 2019 Dyslipidemias Table 1. Lipoproteins
Endocrinology E3
Lipoprotein
Chylomicron VLDL
IDL
LDL HDL
Function
Transports dietary TG from gut to adipose tissue and muscle
Transports hepatic synthesized TG from liver to adipose tissue and muscle
Product of hydrolysis of TG in VLDL by lipoprotein lipase resulting in depletion of TG core Enriched in cholesterol esters
Formed by further removal of residual TG from IDL core by hepatic lipase resulting in greater enriched particles with cholesterol esters
Transports cholesterol from liver to peripheral tissues (gonads, adrenals)
Transports cholesterol from peripheral tissues to liver Acts as a reservoir for apolipoproteins
EXOGENOUS PATHWAY
Bile Acids
Bile acid
x sequestrants
(resins)
ENDOGENOUS PATHWAY
TGs Cholesterol
Oxidized LDL occurs in subendothelial space of arterial blood vessels
EXTRAHEPATIC TISSUES
Cholesterol
AI AII
HDL
Dietary
Dietary
Cholesterol absorption x
Acetyl-CoA
HMG-CoA
x Statin
Endogenous cholesterol
Endocytosis through LDL Receptor
MACROPHAGE
FOAM CELL
EARLY ATHEROSCLEROSIS
inhibitors
SMALL BOWEL
E
LIVER
+ Statin B-100
LDL
Dietary cholesterol
x
Niacin
- apo E - TG
C-II
Endocytosis through B-48 Remnant Receptor
E B-48
Chylomicron Chylomicron Remnant
CAPILLARY
Free Fatty Acids
Hepatic Lipase
TO LIVER
E
C-II B-100
VLDL
E
B-100
IDL
PLASMA LCAT
(IDL gives phospholipids
CAPILLARY
and TG to HDL and receives cholesterol esters from HDL)
Cholesterol
Triglyceride
*LP Lipase requires activation by Apo C-II
Treatment
Refer to treatment of LDL-C/TG at end of section
Refer to treatment of LDL-C/TG at end of section
<10-15% of calories from fat
Supplement with essential fatty acids, fat-soluble vitamins
Plasma transfusion may help individuals with APOC2 mutation
Specific treatment for hepatic lipase deficiency unknown Refer to treatment of LDL-C/TG at end of section
Fibrate + LP Lipase*
degrades TG
Fibrate + LP Lipase*
degrades TG
Free Fatty Acids
Adipose Tissue and Muscle
Adipose Tissue and Muscle
Figure 2. Exogenous and endogenous biosynthetic lipid pathways
Hypertriglyceridemia (Elevated Triglycerides)
PRIMARY HYPERTRIGLYCERIDEMIA
Table 2. Primary Hypertriglyceridemias
Prevalence
Common, Unknown Pathogenesis
Rare, Genetic
Hypertriglyceridemia
Familial hypertriglyceridemia
Familial combined hyperlipidemia
Familial lipoprotein lipase deficiency, Apo-C2 deficiency
Hepatic Lipase Deficiency
Familial dysbetalipoproteinemia (ApoE2/E2)
Labs
↑ TG ↑ VLDL ↓ HDL
↑ TG ↑ VLDL ↑ LDL
↑ TG
↑ Chylomicrons Moderate ↑ in VLDL
↑ TG ↑ HDL ↓ LDL
↑ TG
↑ IDL
↑ Chylomicron remnants
Clinical Presentation
Increased risk of CVD
Obesity, DM2, HTN, hyperinsulinemia, and hyperuricemia in early adulthood
Xanthelasma (10% of cases)
Premature CAD and other vascular disease Obesity
Presents at infancy (LPL), adolescence to adulthood (APOC2) Abdominal complaints (pain, hepatosplenomegaly, pancreatitis)
Lipemia retinalis
Eruptive xanthomata
Unknown if associated with increased risk of atherosclerosis and CAD
Increased CVD risk, tuberous/palmar xanthomata
© Kelly Speck 2016 after Stefania Spano 2012