Page 404 - TNFlipTest
P. 404
GS2 General Surgery and Thoracic Surgery Acronyms Acronyms
Toronto Notes 2019
oesophagogastroduodenoscopy post-operative day
proton pump inhibitor percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography
peptic ulcer disease
small bowel obstruction
small bowel follow-through squamous cell carcinoma syndrome of inappropriate anti-diuretic hormone
superior mesenteric artery superior mesenteric vein
sentinel lymph node biopsy thromboembolic deterrent transesophageal echocardiogram transthoracic echocardiogram upper gastrointestinal bleed
55-FU 5-fluorouracil
AAA abdominal aortic aneurysm
ABG arterial blood gas
ABI ankle brachial index
ALND axillary lymph node dissection
APR abdominoperineal resection
ARDS acute respiratory distress syndrome ATN acute tubular necrosis
BRBPR bright red blood per rectum
BCS breast conserving surgery
CBD common bile duct
CF cystic fibrosis
CHF congestive heart failure
CRC colorectal cancer
CVA costovertebral angle
CVP central venous pressure
DCIS ductal carcinoma in situ
DIC disseminated intravascular coagulation DPL diagnostic peritoneal lavage
DRE digital rectal exam
EBL estimated blood loss ERCP endoscopic retrograde
cholangiopancreatography
EUA examination under anesthesia EUS endoscopic ultrasound
FAP familial adenomatous polyposis FAST focused abdominal sonography for
trauma
FNA fine needle aspiration
FNH focal nodular hyperplasia
FOBT fecal occult blood test
GERD gastroesophageal reflux disease
GI gastrointestinal
GIST gastrointestinal stromal tumour
GU genitourinary
HCC hepatocellular carcinoma
HDGC hereditary diffuse gastric carcinoma HIDA hepatobiliary imino-diacetic acid
HNPCC hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer
IPAH idiopathic pulmonary arterial OGD hypertension POD
IPF idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis PPI IVC inferior vena cava PTC LAR low anterior resection
LBO large bowel obstruction PUD LCIS lobular carcinoma in situ SBO LES lower esophageal sphincter SBFT LGIB lower gastrointestinal bleed SCC LVRS lung volume reduction surgery SIADH MALT mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue
MBP mechanical bowel preparation SMA MEN multiple endocrine neoplasia SMV MIBG metaiodobenzylguanidine SNLB MIS minimally invasive surgery TED MRCP magnetic resonance TEE
cholangiopancreatography TTE
I&D
incision and drainage
MSAFP maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein NGT nasogastric tube
OCP oral contraceptive pill
UGIB
VATS video-assisted thorascopic surgery
Basic Anatomy Review
VIP
vasoactive intestinal
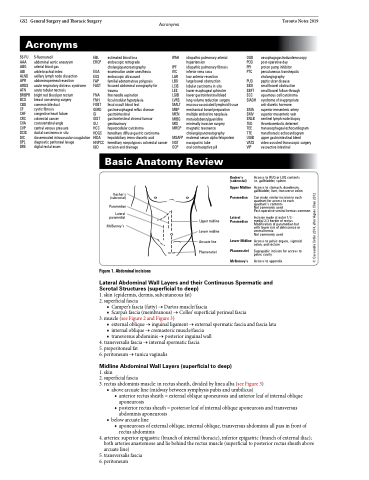
Access to RUQ or LUQ contents i.e. gallbladder, spleen
Access to stomach, duodenum, gallbladder, liver, transverse colon
Can make similar incision in each quadrant for access to each quadrant’s contents
Not commonly used
Post-operative ventral hernias common
Incision made at outer 1/3 - medial 2/3 border of rectus Modification of paramedian but with lower risk of dehiscence or ventral hernia
Access to pelvic organs, sigmoid colon, and rectum
Suprapubic incision for access to pelvic cavity
Access to appendix
Kocher’s (subcostal)
Paramedian
Lateral paramedial
McBurney’s
Figure 1. Abdominal incisions
Upper midline Lower midline Arcuate line Pfannenstiel
Kosher’s (subcostal)
Upper Midline Paramedian
Lateral Paramedian
Lower Midline Pfannenstiel McBurney’s
Not commonly used
Lateral Abdominal Wall Layers and their Continuous Spermatic and Scrotal Structures (superficial to deep)
1. skin (epidermis, dermis, subcutaneous fat)
2. superficial fascia
■ Camper’s fascia (fatty) → Dartos muscle/fascia
■ Scarpa’s fascia (membranous) → Colles’ superficial perineal fascia 3. muscle (see Figure 2 and Figure 3)
■ external oblique → inguinal ligament → external spermatic fascia and fascia lata ■ internal oblique → cremasteric muscle/fascia
■ transversus abdominis → posterior inguinal wall
4. transversalis fascia → internal spermatic fascia 5. preperitoneal fat
6. peritoneum → tunica vaginalis
Midline Abdominal Wall Layers (superficial to deep)
1. skin
2. superficial fascia
3. rectus abdominis muscle: in rectus sheath, divided by linea alba (see Figure 3)
■ above arcuate line (midway between symphysis pubis and umbilicus)
◆ anterior rectus sheath = external oblique aponeurosis and anterior leaf of internal oblique
aponeurosis
◆ posterior rectus sheath = posterior leaf of internal oblique aponeurosis and transversus
abdominis aponeurosis ■ belowarcuateline
◆ aponeuroses of external oblique, internal oblique, transversus abdominis all pass in front of rectus abdominis
4. arteries: superior epigastric (branch of internal thoracic), inferior epigastric (branch of external iliac); both arteries anastomose and lie behind the rectus muscle (superficial to posterior rectus sheath above arcuate line)
5. transversalis fascia 6. peritoneum
© Cassandra Cetlin 2014, after Agnes Chan 2012