Page 506 - TNFlipTest
P. 506
GY20 Gynecology
Ectopic Pregnancy
Toronto Notes 2019
Embryonic demise can be diagnosed by ultrasound based on an intrauterine gestational sac, embryonic crown-rump length ≥7mm, and no cardiac activity
Type
Threatened Inevitable
Incomplete
Complete Missed
Recurrent Septic
History
Vaginal bleeding ± cramping
Increasing bleeding and cramps ± rupture of membranes
Extremely heavy bleeding and cramps ± passage of tissue noticed
Bleeding and complete passage of sac and placenta
No bleeding (fetal death in utero)
≥3 consecutive spontaneous abortions
Contents of uterus infected – infrequent
Clinical
Cervix closed and soft
Cervix closed until products start to expel, then external os opens
Cervix open
Cervix closed, bleeding stopped Cervix closed
Management (± Rhogam®)
Watch and wait <5% go on to abort
a) Watch and wait
b) Misoprostol 400-800 μg PO/PV c) D&C
a) Watch and wait
b) Misoprostol 400-800 μg PO/PV c) D&C
No D&C – expectant management
a) Watch and wait
b) Misoprostol 400-800 μg PO/PV c) D&C
Evaluate mechanical, genetic, environmental, and other risk factors
IV broad spectrum antibiotics for 24 h followed by uterine evacuation
Spontaneous Abortions
• seeTerminationofPregnancyfortherapeuticabortions,GY18 Table 13. Classification of Spontaneous Abortions
Ectopic Pregnancy
Definition
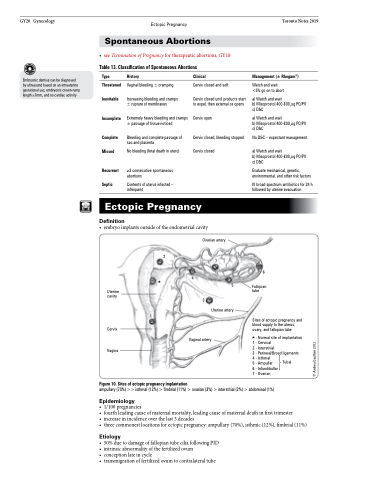
• embryoimplantsoutsideoftheendometrialcavity
Uterine cavity
Cervix
Vagina
5
tube
2
1
Ovarian artery
7 4
3
Uterine artery
Vaginal artery
6
Fallopian
Sites of ectopic pregnancy and blood supply to the uterus, ovary, and fallopian tube
- Normal site of implantation
1 - Cervical
2 - Interstitial
3 - Perineal/Broad ligaments
4 - Isthmal
5 - Ampullar
6 - Infundibullar
7 - Ovarian
Tubal
• 1/100pregnancies
• fourthleadingcauseofmaternalmortality,leadingcauseofmaternaldeathinfirsttrimester
• increaseinincidenceoverthelast3decades
• threecommonestlocationsforectopicpregnancy:ampullary(70%),isthmic(12%),fimbrial(11%)
Etiology
• 50%duetodamageoffallopiantubeciliafollowingPID • intrinsicabnormalityofthefertilizedovum
• conceptionlateincycle
• transmigrationoffertilizedovumtocontralateraltube
Figure 10. Sites of ectopic pregnancy implantation
ampullary (70%) >> isthmal (12%) > fimbrial (11%) > ovarian (3%) > interstitial (2%) > abdominal (1%)
Epidemiology
© Andrea Gauthier 2012