Page 542 - TNFlipTest
P. 542
H2 Hematology Acronyms
AFib atrial fibrillation
AFLP acute fatty liver of pregnancy
AIHA autoimmune hemolytic anemia
ALL acute lymphoblastic leukemia
ALPA antiphospholipid antibodies
AML acute myeloid leukemia
ANC absolute neutrophil count
APC activated protein C
APCR activated protein C resistance
APS antiphospholipid antibody syndrome aPTT activated partial thromboplastin time ARDS acute respiratory syndrome
BM bone marrow
CBC complete blood count
CHF congestive heart failure
CLL chronic lymphocytic leukemia
CML chronic myeloid leukemia
CRP C-reactive protein
DIC disseminated intravascular coagulation EPO erythropoietin
ESR erythrocyte sedimentation rate
ET essential thrombocythemia
FNA fine needle aspiration
G6PD glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase G-CSF granulocyte-colony stimulating factor GSH glutathione
HA hemolytic anemia
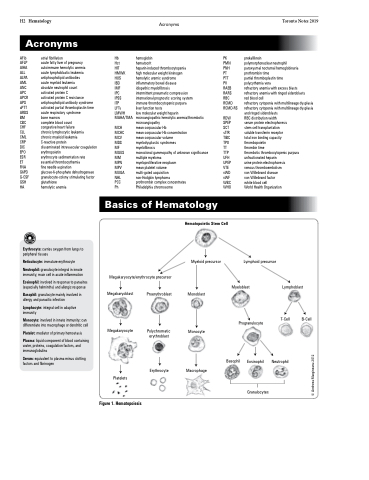
Erythrocyte: carries oxygen from lungs to peripheral tissues
Reticulocyte: immature erythrocyte Neutrophil: granulocyte integral in innate
immunity; main cell in acute inflammation
Eosinophil: involved in response to parasites (especially helminths) and allergic response
Basophil: granulocyte mainly involved in allergy and parasitic infection
Lymphocyte: integral cell in adaptive immunity
Monocyte: involved in innate immunity; can differentiate into macrophage or dendritic cell
Platelet: mediator of primary hemostasis
Plasma: liquid component of blood containing water, proteins, coagulation factors, and immunoglobulins
Serum: equivalent to plasma minus clotting factors and fibrinogen
Acronyms
Hb hemoglobin PK
Hct hematocrit PMN
HIT heparin-induced thrombocytopenia PNH HMWK high molecular weight kininogen PT
HUS hemolytic uremic syndrome PTT
IBD inflammatory bowel disease PV
IMF idiopathic myelofibrosis RAEB
IPC intermittent pneumatic compression RARS IPSS international prognostic scoring system RBC
ITP immune thrombocytopenic purpura RCMD LFTs liver function tests RCMD-RS LMWH low molecular weight heparin
MAHA/TMA microangiopathic hemolytic anemia/thrombotic RDW
microangiopathy SPEP MCH mean corpuscular Hb SCT MCHC mean corpuscular Hb concentration sTfR MCV mean corpuscular volume TIBC MDS myelodysplastic syndromes TPO MF myelofibrosis TT MGUS monoclonal gammopathy of unknown significance TTP MM multiple myeloma UFH MPN myeloproliferative neoplasm UPEP MPV mean platelet volume VTE MUGA multi-gated acquisition vWD NHL non-Hodgkin lymphoma vWF PCC prothrombin complex concentrates WBC Ph Philadelphia chromosome WHO
Basics of Hematology
Toronto Notes 2019
prekallikrein
polymorphonuclear neutrophil
paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria prothrombin time
partial thromboplastin time
polycythemia vera
refractory anemia with excess blasts
refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts
red blood cell
refractory cytopenia with multilineage dysplasia refractory cytopenia with multilineage dysplasia and ringed sideroblasts
RBC distribution width
serum protein electrophoresis
stem cell transplantation
soluble transferrin receptor
total iron binding capacity
thrombopoietin
thrombin time
thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura unfractionated heparin
urine protein electrophoresis
venous thromboembolism
von Willebrand disease
von Willebrand factor
white blood cell
World Health Organization
Hematopoietic Stem Cell
Myeloid precursor
Monoblast
Monocyte
Macrophage
Lymphoid precursor
Megakaryocyte/erythrocyte precursor
Megakaryoblast
Megakaryocyte
Platelets
Figure 1. Hematopoiesis
Proerythroblast
Polychromatic erythroblast
Erythrocyte
Myeloblast
Progranulocyte
Lymphoblast
T-Cell B-Cell
Neutrophil
Basophil
Eosinophil
Granulocytes
© Andreea Margineanu 2012