Page 597 - TNFlipTest
P. 597
Toronto Notes 2019
Common Medications
Hematology H57
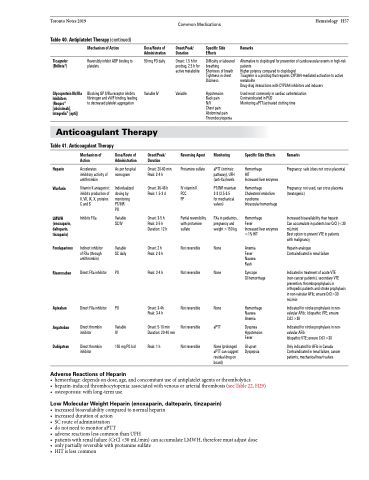
Table 40. Antiplatelet Therapy (continued)
Ticagrelor (Brilinta®)
Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa Inhibitors
(Reopro® [abciximab], Integrelin® [epti])
Specific Side Effects
Difficulty or laboured breathing
Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Dizziness
Hypotension
Back pain
N/V
Chest pain Abdominal pain Thrombocytopenia
Monitoring
aPTT (intrinsic pathway), UFH (anti-Xa) levels
PT/INR maintain 2-3 (2.5-3.5
for mechanical valves)
FXa in pediatrics, pregnancy and weight >150 kg
None
None
None
aPTT
None (prolonged aPTT can suggest residual drug on board)
Remarks
Alternative to clopidogrel for prevention of cardiovascular events in high-risk patients
Higher potency compared to clopidogrel
Ticagrelor is a prodrug that requires CYP3A4-mediated activation to active metabolite
Drug-drug interactions with CYP3A4 inhibitors and inducers
Used most commonly in cardiac catheterization Contraindicated in PUD
Monitoring aPTT/activated clotting time
Mechanism of Action
Reversibly inhibit ADP binding to platelets
Blocking GP II/IIIa receptor inhibits fibrinogen and vWF binding, leading to decreased platelet aggregation
Dose/Route of Administration
90 mg PO daily
Variable IV
Onset/Peak/ Duration
Onset: 1.5 h for prodrug, 2.5 h for active metabolite
Variable
Reversing Agent
Protamine sulfate
IV vitamin K PCC
FP
Partial reversibility with protamine sulfate
Not reversible
Not reversible
Not reversible Not reversible Not reversible
Anticoagulant Therapy
Table 41. Anticoagulant Therapy
Mechanism of Action
Accelerates inhibitory activity of antithrombin
Vitamin K antagonist: inhibits production of II, VII, IX, X, proteins C and S
Inhibits FXa
Indirect inhibitor of FXa (through antithrombin)
Direct FXa inhibitor
Direct FXa inhibitor
Direct thrombin inhibitor
Direct thrombin inhibitor
Dose/Route of Administration
As per hospital nomogram
Individualized dosing by monitoring PT/INR
PO
Variable SC/IV
Variable SC daily
PO
PO
Variable IV
150 mg PO bid
Onset/Peak/ Duration
Onset: 20-60 Peak: 2-4 h
Onset: 36-48 Peak: 1.5-3 d
Onset: 3-5 h Peak: 3-5 h Duration: 12 h
Onset: 2 h Peak: 2-3 h
Peak: 2-4 h
Onset: 3-4h Peak: 3-4 h
Onset: 5-10 min Duration: 20-40 min
Peak: 1 h
Specific Side Effects
Hemorrhage
HIT
Increased liver enzymes
Hemorrhage Cholesterol embolism syndrome
Intraocular hemorrhage
Hemorrhage
Fever
Increased liver enzymes <1% HIT
Anemia Fever Nausea Rash
Syncope
GI hemorrhage
Hemorrhage Nausea Anemia
Dyspnea Hypotension Fever
GI upset Dyspepsia
Remarks
Pregnancy: safe (does not cross placenta)
Pregnancy: not used, can cross placenta (teratogenic)
Increased bioavailability than heparin
Can accumulate in patients low CrCl (<30 mL/min)
Best option to prevent VTE in patients with malignancy
Heparin analogue Contraindicated in renal failure
Indicated in treatment of acute VTE (non-cancer patients), secondary VTE prevention, thromboprophylaxis in orthopedic patients and stroke prophylaxis in non-valvular AFib; ensure CrCl>30 mL/min
Indicated for stroke prophylaxis in non- valvular AFib; Idiopathic VTE; ensure CrCl >30
Indicated for stroke prophylaxis in non- valvular AFib
Idiopathic VTE; ensure CrCl >30
Only indicated for AFib in Canada Contraindicated in renal failure, cancer patients, mechanical heart valves
Heparin Warfarin
LMWH (enoxaparin, dalteparin, tinzaparin)
Fondaparinux
Rivaroxaban
Apixaban Argatroban Dabigatran
min h
Adverse Reactions of Heparin
• hemorrhage:dependsondose,age,andconcomitantuseofantiplateletagentsorthrombolytics
• heparin-inducedthrombocytopenia:associatedwithvenousorarterialthrombosis(seeTable22,H29) • osteoporosis:withlong-termuse
Low Molecular Weight Heparin (enoxaparin, dalteparin, tinzaparin)
• increasedbioavailabilitycomparedtonormalheparin • increaseddurationofaction
• SCrouteofadministration
• donotneedtomonitoraPTT
• adversereactionslesscommonthanUFH
• patientswithrenalfailure(CrCl<30mL/min)canaccumulateLMWH,thereforemustadjustdose • onlypartiallyreversiblewithprotaminesulfate
• HITislesscommon