Page 598 - TNFlipTest
P. 598
H58 Hematology
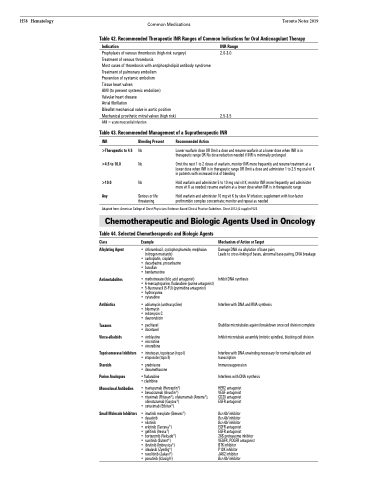
Common Medications Toronto Notes 2019 Table 42. Recommended Therapeutic INR Ranges of Common Indications for Oral Anticoagulant Therapy
Indication
Prophylaxis of venous thrombosis (high-risk surgery)
Treatment of venous thrombosis
Most cases of thrombosis with antiphospholipid antibody syndrome Treatment of pulmonary embolism
Prevention of systemic embolism
Tissue heart valves
AMI (to prevent systemic embolism)
Valvular heart disease
Atrial fibrillation
Bileaflet mechanical valve in aortic position
Mechanical prosthetic mitral valves (high risk)
AMI = acute myocardial infarction
INR Range
2.0-3.0
2.5-3.5
Table 43. Recommended Management of a Supratherapeutic INR
INR
>Therapeutic to 4.5 >4.5 to 10.0
>10.0 Any
Bleeding Present
No No
No
Serious or life threatening
Recommended Action
Lower warfarin dose OR Omit a dose and resume warfarin at a lower dose when INR is in therapeutic range OR No dose reduction needed if INR is minimally prolonged
Omit the next 1 to 2 doses of warfarin, monitor INR more frequently and resume treatment at a lower dose when INR is in therapeutic range OR Omit a dose and administer 1 to 2.5 mg oral vit K in patients with increased risk of bleeding
Hold warfarin and administer 5 to 10 mg oral vit K; monitor INR more frequently and administer more vit K as needed; resume warfarin at a lower dose when INR is in therapeutic range
Hold warfarin and administer 10 mg vit K by slow IV infusion; supplement with four-factor prothrombin complex concentrate; monitor and repeat as needed
Adapted from: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest 2012;(2 suppl):e152S
Chemotherapeutic and Biologic Agents Used in Oncology
Table 44. Selected Chemotherapeutic and Biologic Agents
Class
Alkylating Agent
Antimetabolites
Antibiotics
Taxanes Vinca-alkaloids
Topoisomerase Inhibitors Steroids
Purine Analogues Monoclonal Antibodies
Small Molecule Inhibitors
Example
• chlorambucil, cyclophosphamide, melphalan (nitrogen mustards)
• carboplatin, cisplatin
• dacarbazine, procarbazine • busulfan
• bendamustine
• methotrexate (folic acid antagonist)
• 6-mercaptopurine,fludarabine(purineantagonist) • 5-fluorouracil(5-FU)(pyrimidineantagonist)
• hydroxyurea
• cytarabine
• adriamycin (anthracycline) • bleomycin
• mitomycinC
• daunorubicin
• paclitaxel • docetaxel
• vinblastine • vincristine • vinorelbine
• irinotecan, topotecan (topo I) • etoposide (topo II)
• prednisone
• dexamethasone
• fludarabine • cladribine
• trastuzumab (Herceptin®)
• bevacizumab (Avastin®)
• rituximab (Rituxan®), ofatumumab (Arzerra®),
obinutuzumab (Gayzva®) • cetuximab(Erbitux®)
• imatinib mesylate (Gleevec®) • dasatinib
• nilotinib
• erlotinib (Tarceva®)
• gefitinib (Iressa®)
• bortezomib (Velcade®) • sunitinib (Sutent®)
• ibrutinib (Imbruvica®) • idealasib (Zyedlig®)
• ruxolitinib (Jakavi®) • ponatinib (Iclusig®)
Mechanism of Action or Target
Damage DNA via alkylation of base pairs
Leads to cross-linking of bases, abnormal base-pairing, DNA breakage
Inhibit DNA synthesis
Interfere with DNA and RNA synthesis
Stabilize microtubules against breakdown once cell division complete Inhibit microtubule assembly (mitotic spindles), blocking cell division
Interfere with DNA unwinding necessary for normal replication and transcription
Immunosuppression
Interferes with DNA synthesis
HER2 antagonist VEGF antagonist CD20 antagonist EGFR antagonist
Bcr-Abl inhibitor
Bcr-Abl inhibitor
Bcr-Abl inhibitor
EGFR antagonist
EGFR antagonist
26S proteasome inhibitor VEGFR, PDGFR antagonist BTK inhibitor
P13K inhibitor JAK2 inhibitor Bcr-Abl inhibitor