Page 599 - TNFlipTest
P. 599
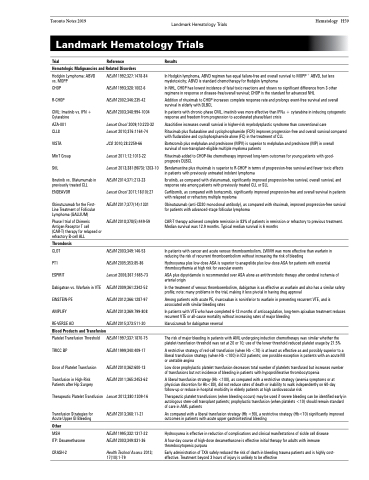
Toronto Notes 2019 Landmark Hematology Trials Hematology H59 Landmark Hematology Trials
Trial Reference
Hematologic Malignancies and Related Disorders
Results
In Hodgkin lymphoma, ABVD regimen has equal failure-free and overall survival to MOPP + ABVD, but less myelotoxicity; ABVD is standard chemotherapy for Hodgkin lymphoma
In NHL, CHOP has lowest incidence of fatal toxic reactions and shows no significant difference from 3 other regimens in response or disease-free/overall survival; CHOP is the standard for advanced NHL
Addition of rituximab to CHOP increases complete response rate and prolongs event-free survival and overall survival in elderly with DLBCL
In patients with chronic-phase CML, imatinib was more effective than IFNα + cytarabine in inducing cytogenetic response and freedom from progression to accelerated phase/blast crisis
Azacitidine increases overall survival in higher-risk myelodysplastic syndrome than conventional care
Rituximab plus fludarabine and cyclophosphamide (FCR) improves progression-free and overall survival compared with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide alone (FC) in the treatment of CLL
Bortezomib plus melphalan and prednisone (MPV) is superior to melphalan and prednisone (MP) in overall survival of non-transplant-eligible multiple myeloma patients
Rituximab added to CHOP-like chemotherapy improved long-term outcomes for young patients with good- prognosis DLBCL
Bendamustine plus rituximab is superior to R-CHOP in terms of progression-free survival and fewer toxic effects in patients with previously untreated indolent lymphoma
Ibrutinib, as compared with ofatumumab, significantly improved progression-free survival, overall survival, and response rate among patients with previously treated CLL or SLL
Carfilzomib, as compared with bortezomib, significantly improved progression-free and overall survival in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma
Obinutuzumab (anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody), as compared with rituximab, improved progression-free survival for patients with advanced-stage follicular lymphoma
CAR-T therapy achieved complete remission in 83% of patients in remission or refractory to previous treatment. Median survival was 12.9 months. Typical median survival is 6 months
In patients with cancer and acute venous thromboembolism, LWMH was more effective than warfarin in reducing the risk of recurrent thromboembolism without increasing the risk of bleeding
Hydroxyurea plus low-dose ASA is superior to anagrelide plus low-dose ASA for patients with essential thrombocythemia at high risk for vascular events
ASA plus dipyridamole is recommended over ASA alone as antithrombotic therapy after cerebral ischemia of arterial origin
In the treatment of venous thromboembolism, dabigatran is as effective as warfarin and also has a similar safety profile; note: many problems in the trial, making it less pivotal in having drug approval
Among patients with acute PE, rivaroxaban is noninferior to warfarin in preventing recurrent VTE, and is associated with similar bleeding rates
In patients with VTE who have completed 6-12 months of anticoagulation, long-term apixaban treatment reduces recurrent VTE or all-cause mortality without increasing rates of major bleeding
Idarucizumab for dabigatran reversal
The risk of major bleeding in patients with AML undergoing induction chemotherapy was similar whether the platelet-transfusion threshold was set at 20 or 10; use of the lower threshold reduced platelet usage by 21.5%
A restrictive strategy of red-cell transfusion (when Hb <70) is at least as effective as and possibly superior to a liberal transfusion strategy (when Hb <100) in ICU patients; one possible exception is patients with an acute MI or unstable angina
Low dose prophylactic platelet transfusion decreases total number of platelets transfused but increases number of transfusions but not incidence of bleeding in patients with hypoproliferative thrombocytopenia
A liberal transfusion strategy (Hb <100), as compared with a restrictive strategy (anemia symptoms or at physician discretion for Hb<80), did not reduce rates of death or inability to walk independently on 60-day follow-up or reduce in-hospital morbidity in elderly patients at high cardiovascular risk
Therapeutic platelet transfusions (when bleeding occurs) may be used if severe bleeding can be identified early in autologous stem-cell transplant patients; prophylactic transfusion (when platelets <10) should remain standard of care in AML patients
As compared with a liberal transfusion strategy (Hb <90), a restrictive strategy (Hb<70) significantly improved outcomes in patients with acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding
Hydroxyurea is effective in reduction of complications and clinical manifestations of sickle cell disease
A four-day course of high-dose dexamethasone is effective initial therapy for adults with immune thrombocytopenic purpura
Early administration of TXA safely reduced the risk of death in bleeding trauma patients and is highly cost- effective. Treatment beyond 3 hours of injury is unlikely to be effective
Hodgkin Lymphoma: ABVD vs. MOPP
CHOP R-CHOP
CML: Imatinib vs. IFN + Cytarabine
AZA-001 CLL8
VISTA
MInT Group
StIL
Ibrutinib vs. Ofatumumab in previously treated CLL
ENDEAVOR
Obinutuzumab for the First- Line Treatment of Follicular Lymphoma (GALLIUM)
Phase I trial of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T cell (CAR-T) therapy for relapsed or refractory B-cell ALL
Thrombosis
CLOT
PT1
ESPIRIT
Dabigatran vs. Warfarin in VTE EINSTEIN-PE
AMPLIFY
RE-VERSE AD
Blood Products and Transfusion
Platelet Transfusion Threshold TRICC BP
Dose of Platelet Transfusion
Transfusion in High-Risk Patients after Hip Surgery
Therapeutic Platelet Transfusion
Transfusion Strategies for Acute Upper GI Bleeding
Other
MSH
ITP: Dexamethasone
CRASH-2
NEJM 1992;327:1478-84
NEJM 1993;328:1002-6
NEJM 2002;346:235-42
NEJM 2003;348:994-1004
Lancet Oncol 2009;10:223-32 Lancet 2010;376:1164-74
JCO 2010;28:2259-66
Lancet 2011;12:1013-22
Lancet 2013;381(9873):1203-10 NEJM 2014;371:213-23
Lancet Oncol 2017;18(10):27 NEJM 2017;377(14):1331
NEJM 2018;378(5):449-59
NEJM 2003;349:146-53 NEJM 2005;353:85-86 Lancet 2006;367:1665-73 NEJM 2009;361:2342-52 NEJM 2012;366:1287-97 NEJM 2013;369:799-808 NEJM 2015;373:511-20
NEJM 1997;337:1870-75 NEJM 1999;340:409-17
NEJM 2010;362:600-13 NEJM 2011;365:2453-62
Lancet 2012;380:1309-16 NEJM 2013;368:11-21
NEJM 1995;332:1317-22 NEJM 2003;349:831-36
Health Technol Assess 2013; 17(10):1-79