Page 650 - TNFlipTest
P. 650
ID50 Infectious Diseases
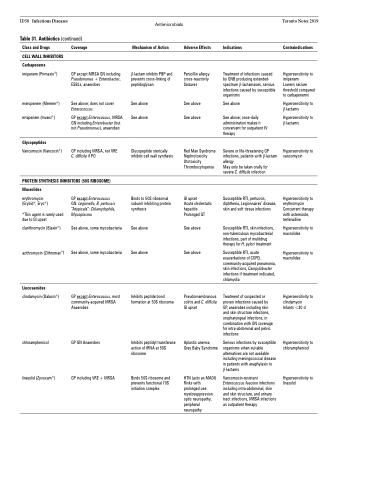
Table 31. Antibiotics (continued)
Antimicrobials
Mechanism of Action
β-lactam inhibits PBP and prevents cross-linking of peptidoglycan
See above
See above
Glycopeptide sterically inhibits cell wall synthesis
Binds to 50S ribosomal subunit inhibiting protein synthesis
See above
See above
Inhibits peptide bond formation at 50S ribosome
Inhibits peptidyl transferase action of tRNA at 50S ribosome
Binds 50S ribosome and prevents functional 70S initiation complex
Toronto Notes 2019
Class and Drugs
CELL WALL INHIBITORS
Carbapenems
imipenem (Primaxin®)
meropenem (Merrem®) ertapenem (Invanz®)
Glycopeptides
Vancomycin (Vancocin®)
Coverage
GP except MRSA GN including Pseudomonas + Enterobacter, ESBLs, anaerobes
See above; does not cover
Enterococcus
GP except Enterococcus, MRSA GN including Enterobacter (but not Pseudomonas), anaerobes
GP including MRSA, not VRE C. difficile if PO
Adverse Effects
Penicillin allergy cross-reactivity Seizures
See above
See above
Red Man Syndrome Nephrotoxicity Ototoxicity Thrombocytopenia
GI upset
Acute cholestatic hepatitis Prolonged QT
See above
See above
Pseudomembranous colitis and C. difficile GI upset
Aplastic anemia Grey Baby Syndrome
HTN (acts as MAOI) Risks with prolonged use: myelosuppression optic neuropathy, peripheral neuropathy
Indications
Treatment of infections caused by GNB producing extended- spectrum β-lactamases, serious infections caused by susceptible organisms
See above
See above; once-daily administration makes it convenient for outpatient IV therapy
Severe or life-threatening GP infections, patients with β-lactam allergy
May only be taken orally for severe C. difficile infection
Susceptible RTI, pertussis, diphtheria, Legionnaires’ disease, skin and soft tissue infections
Susceptible RTI, skin infections, non-tuberculous mycobacterial infections, part of mulitdrug therapy for H. pylori treatment
Susceptible RTI, acute exacerbations of COPD, community-acquired pneumonia, skin infections, Campylobacter infections if treatment indicated, chlamydia
Treatment of suspected or proven infections caused by GP, anaerobes including skin and skin structure infections, oropharyngeal infections, in combination with GN coverage for intra-abdominal and pelvic infections
Serious infections by susceptible organisms when suitable alternatives are not available including meningococcal disease in patients with anaphylaxis to β-lactams
Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium infections including intra-abdominal, skin and skin structure, and urinary tract infections, MRSA infections as outpatient therapy
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to imipenem
Lowers seizure threshold compared to carbapenems
Hypersensitivity to β-lactams
Hypersensitivity to β-lactams
Hypersensitivity to vancomycin
Hypersensitivity to erythromycin Concurrent therapy with astemizole, terfenadine
Hypersensitivity to macrolides
Hypersensitivity to macrolides
Hypersensitivity to clindamycin Infants <30 d
Hypersensitivity to chloramphenicol
Hypersensitivity to linezolid
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS INHIBITORS (50S RIBOSOME)
Macrolides
erythromycin (Erybid®, Eryc®)
*This agent is rarely used due to GI upset
clarithromycin (Biaxin®)
azithromycin (Zithromax®)
Lincosamides
clindamycin (Dalacin®)
chloramphenicol
linezolid (Zyvoxam®)
GP except Enterococcus GN: Legionella, B. pertussis “Atypicals”: Chlamydophila, Mycoplasma
See above, some mycobacteria
See above, some mycobacteria
GP except Enterococcus, most community-acquired MRSA Anaerobes
GP GN Anaerobes
GP including VRE + MRSA