Page 652 - TNFlipTest
P. 652
ID52 Infectious Diseases
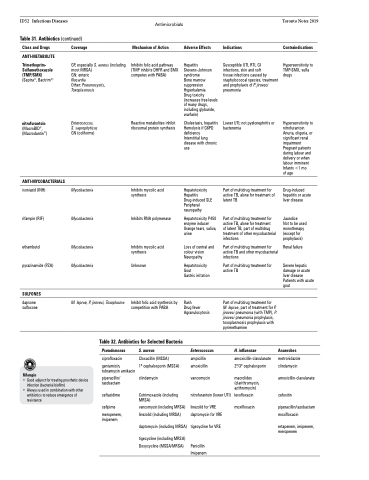
Table 31. Antibiotics (continued)
Antimicrobials
Mechanism of Action
Inhibits folic acid pathway (TMP inhibits DHFR and SMX competes with PABA)
Reactive metabolites inhibit ribosomal protein synthesis
Inhibits mycolic acid synthesis
Inhibits RNA polymerase
Inhibits mycolic acid synthesis
Unknown
Inhibit folic acid synthesis by competition with PABA
Toronto Notes 2019
Class and Drugs
ANTI-METABOLITE
Trimethoprim- Sulfamethoxazole (TMP/SMX) (Septra®, Bactrim®)
nitrofurantoin
(MacroBID®, (Macrodantin®)
ANTI-MYCOBACTERIALS
isoniazid (INH)
rifampin (RIF)
ethambutol pyrazinamide (PZA)
SULFONES
dapsone sulfoxone
Rifampin
• Good adjunct for treating prosthetic device infection (bacterial biofilm)
• Always used in combination with other antibiotics to reduce emergence of resistance
Coverage
GP, especially S. aureus (including most MRSA)
GN: enteric
Nocardia
Other: Pneumocystis, Toxoplasmosis
Enterococcus, S. saprophyticus GN (coliforms)
Mycobacteria
Mycobacteria
Mycobacteria Mycobacteria
M. leprae, P. jiroveci, Toxoplasma
Adverse Effects
Hepatitis Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Bone marrow suppression Hyperkalemia
Drug toxicity (increases free levels of many drugs, including glyburide, warfarin)
Cholestasis, hepatitis Hemolysis if G6PD deficiency
Interstitial lung disease with chronic use
Hepatotoxicity Hepatitis Drug-induced SLE Peripheral neuropathy
Hepatotoxicity P450 enzyme inducer Orange tears, saliva, urine
Loss of central and colour vision Neuropathy
Hepatotoxicity Gout
Gastric irritation
Rash
Drug fever Agranulocytosis
Enterococcus
ampicillin amoxicillin
vancomycin
nitrofurantoin (lower UTI)
linezolid for VRE daptomycin for VRE
tigecycline for VRE
Penicillin Imipenem
Table 32. Antibiotics for Selected Bacteria
Indications
Susceptible UTI, RTI, GI infections, skin and soft
tissue infections caused by staphylococcal species, treatment and prophylaxis of P. jiroveci pneumonia
Lower UTI; not pyelonephritis or bacteremia
Part of multidrug treatment for active TB, alone for treatment of latent TB
Part of multidrug treatment for active TB, alone for treatment
of latent TB, part of multidrug treatment of other mycobacterial infections
Part of multidrug treatment for active TB and other mycobacterial infections
Part of multidrug treatment for active TB
Part of multidrug treatment for M. leprae, part of treatment for P. jiroveci pneumonia (with TMP), P. jiroveci pneumonia prophylaxis, toxoplasmosis prophylaxis with pyrimethamine
H. influenzae
amoxicillin-clavulanate 2o/3o cephalosporin
macrolides (clarithromycin, azithromycin)
levofloxacin moxifloxacin
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to TMP-SMX, sulfa drugs
Hypersensitivity to nitrofurantoin Anuria, oliguria, or significant renal impairment Pregnant patients during labour and delivery or when labour imminent Infants <1 mo
of age
Drug-induced hepatitis or acute liver disease
Jaundice
Not to be used monotherapy (except for prophylaxis)
Renal failure
Severe hepatic damage or acute liver disease Patients with acute gout
Anaerobes
metronidazole clindamycin
amoxicillin-clavulanate
cefoxitin
piperacillin/tazobactam moxifloxacin
ertapenem, imipenem, meropenem
Pseudomonas
ciprofloxacin
gentamicin, tobramycin amikacin
piperacillin/ tazobactam
ceftazidime
cefipime
meropenem, imipenem
S. aureus
Cloxacillin (MSSA)
1o cephalosporin (MSSA)
clindamycin
Cotrimoxazole (including MRSA)
vancomycin (including MRSA) linezolid (including MRSA)
daptomycin (including MRSA)
tigecycline (including MRSA) Doxycycline (MSSA/MRSA)