Page 653 - TNFlipTest
P. 653
Toronto Notes 2019
Antivirals
Infectious Diseases ID53
Antivirals
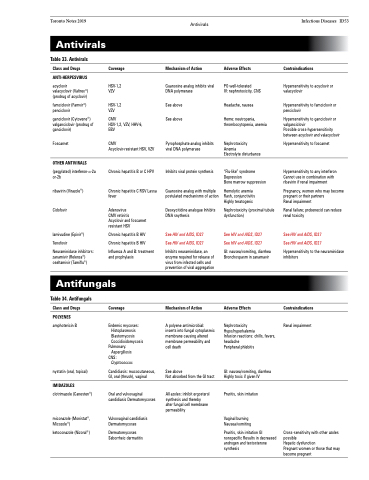
Table 33. Antivirals
Class and Drugs
ANTI-HERPESVIRUS
acyclovir
valacyclovir (Valtrex®) (prodrug of acyclovir)
famciclovir (Famvir®) penciclovir
ganciclovir (Cytovene®) valganciclovir (prodrug of ganciclovir)
Foscarnet
OTHER ANTIVIRALS
(pegylated) interferon-α-2a or-2b
ribavirin (Virazole®) Cidofovir
lamivudine (Epivir®)
Tenofovir
Neuraminidase inhibitors: zanamivir (Relenza®) oseltamivir (Tamiflu®)
Coverage
HSV-1,2 VZV
HSV-1,2 VZV
CMV
HSV-1,2, VZV, HHV-6, EBV
CMV
Acyclovir-resistant HSV, VZV
Chronic hepatitis B or C HPV
Chronic hepatitis C RSV Lassa fever
Adenovirus
CMV retinitis
Acyclovir and foscarnet resistant HSV
Chronic hepatitis B HIV Chronic hepatitis B HIV
Influenza A and B: treatment and prophylaxis
Mechanism of Action
Guanosine analog inhibits viral DNA polymerase
See above See above
Pyrophosphate analog inhibits viral DNA polymerase
Inhibits viral protein synthesis
Guanosine analog with multiple postulated mechanisms of action
Deoxycitidine analogue Inhibits DNA snythesis
See HIV and AIDS, ID27 See HIV and AIDS, ID27
Inhibits neuraminidase, an enzyme required for release of virus from infected cells and prevention of viral aggregation
Mechanism of Action
A polyene antimicrobial: inserts into fungal cytoplasmic membrane causing altered membrane permeability and cell death
See above
Not absorbed from the GI tract
All azoles: inhibit ergosterol synthesis and thereby
alter fungal cell membrane permeability
Adverse Effects
PO well-tolerated
IV: nephrotoxicity, CNS
Headache, nausea
Heme: neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia
Nephrotoxicity Anemia
Electrolyte disturbance
“Flu-like” syndrome Depression
Bone marrow suppression
Hemolytic anemia Rash, conjunctivitis Highly teratogenic
Nephrotoxicity (proximal tubule dysfunction)
See HIV and AIDS, ID27
See HIV and AIDS, ID27
GI: nausea/vomiting, diarrhea Bronchospasm in zanamavir
Adverse Effects
Nephrotoxicity Hypo/hyperkalemia
Infusion reactions: chills, fevers, headache
Peripheral phlebitis
GI: nausea/vomiting, diarrhea Highly toxic if given IV
Pruritis, skin irritation
Vaginal burning Nausea/vomiting
Pruritis, skin irritation GI nonspecific Results in decreased androgen and testosterone synthesis
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to acyclovir or valacyclovir
Hypersensitivity to famciclovir or penciclovir
Hypersensitivity to ganciclovir or valganciclovir
Possible cross-hypersensitivity between acyclovir and valacyclovir
Hypersensitivity to foscarnet
Hypersensitivity to any interferon Cannot use in combination with ribavirin if renal impairment
Pregnancy, women who may become pregnant or their partners
Renal impairment
Renal failure; probenecid can reduce renal toxicity
See HIV and AIDS, ID27 See HIV and AIDS, ID27
Hypersensitivity to the neuraminidase inhibitors
Contraindications
Renal impairment
Antifungals
Table 34. Antifungals
Class and Drugs
POLYENES
amphotericin B
nystatin (oral, topical)
IMIDAZOLES
clotrimazole (Canesten®)
miconazole (Monistat®, Micozole®)
ketoconazole (Nizoral®)
Coverage
Endemic mycoses: Histoplasmosis Blastomycosis Coccidioidomycosis
Pulmonary: Aspergillosis
CNS:
Cryptococcus
Candidiasis: mucocutaneous, GI, oral (thrush), vaginal
Oral and vulvovaginal candidiasis Dermatomycoses
Vulvovaginal candidiasis Dermatomycoses
Dermatomycoses Seborrheic dermatitis
Cross-sensitivity with other azoles possible
Hepatic dysfunction
Pregnant women or those that may become pregnant