Page 651 - TNFlipTest
P. 651
Toronto Notes 2019
Antimicrobials
Infectious Diseases ID51
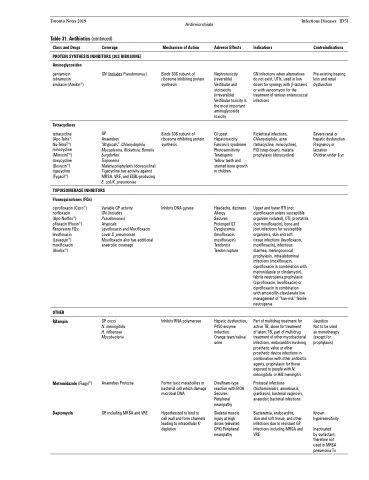
Table 31. Antibiotics (continued)
Class and Drugs Coverage
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS INHIBITORS (30S RIBOSOME)
Mechanism of Action
Binds 30S subunit of ribosome inhibiting protein synthesis
Binds 30S subunit of ribosome inhibiting protein synthesis
Inhibits DNA gyrase
Adverse Effects
Nephrotoxicity (reversible) Vestibular and ototoxicity (irreversible) Vestibular toxicity is the most important aminoglycoside toxicity
GI upset Hepatotoxicity Fanconi’s syndrome Photosensitivity Teratogenic
Yellow teeth and stunted bone growth in children
Headache, dizziness Allergy
Seizures
Prolonged QT Dysglycemia (levofloxacin, moxifloxacin) Tendonitis
Tendon rupture
Hepatic dysfunction, P450 enzyme induction
Orange tears/saliva/ urine
Disulfiram-type reaction with EtOH Seizures Peripheral neuropathy
Skeletal muscle injury at high doses (elevated CPK) Peripheral neuropathy
Indications
GN infections when alternatives do not exist, UTIs, used in low doses for synergy with β-lactams or with vancomycin for the treatment of serious enterococcal infections
Rickettsial infections, Chlamydophila, acne (tetracycline, minocycline), PID (step-down), malaria prophylaxis (doxycycline)
Upper and lower RTI (not ciprofloxacin unless susceptible organism isolated), UTI, prostatitis (not moxifloxacin), bone and
joint infections for susceptible organisms, skin and soft
tissue infections (levofloxacin, moxifloxacin), infectious
diarrhea, meningococcal prophylaxis, intra-abdominal infections (moxifloxacin, ciprofloxacin in combination with metronidazole or clindamycin), febrile neutropenia prophylaxis (ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin) or ciprofloxacin in combination
with amoxicillin-clavulanate low management of “low-risk” febrile neutropenia
Part of multidrug treatment for active TB, alone for treatment
of latent TB, part of multidrug treatment of other mycobacterial infections, endocarditis involving prosthetic valve or other prosthetic device infections in combination with other antibiotic agents, prophylaxis for those exposed to people with N. meningitidis or HiB meningitis
Protozoal infections (trichomoniasis, amoebiasis, giardiasis), bacterial vaginosis, anaerobic bacterial infections
Bacteremia, endocarditis,
skin and soft tissue, and other infections due to resistant GP infections including MRSA and VRE
Contraindications
Pre-existing hearing loss and renal dysfunction
Severe renal or hepatic dysfunction Pregnancy or lactation
Children under 8 yr
Aminoglycosides
gentamicin tobramycin amikacin (Amikin®)
Tetracyclines
tetracycline (Apo-Tetra®, Nu-TetraT®) minocycline (MinocinT®) doxycycline (Doxycin®) tigecycline (Tygacil®)
GN (includes Pseudomonas)
GP
Anaerobes
“Atypicals”: Chlamydophila, Mycoplasma, Rickettsia, Borrelia burgdorferi
Treponema
Malaria prophylaxis (doxycycline) Tigecycline has activity against MRSA, VRE, and ESBL-producing E. coli/K. pneumoniae
TOPOISOMERASE INHIBITORS
Fluoroquinolones (FQs)
ciprofloxacin (Cipro®) norfloxacin (Apo-Norflox®) ofloxacin (Floxin®) Respiratory FQs: levofloxacin (Levaquin®) moxifloxacin (Avelox®)
OTHER
Rifampin
Metronidazole (Flagyl®)
Daptomycin
Variable GP activity
GN (includes
Pseudomonas)
Atypicals
Levofloxacin and Moxifloxacin cover S. pneumoniae Moxifloxacin also has additional anaerobic coverage
GP cocci
N. meningitidis H. influenzae Mycobacteria
Anaerobes Protozoa
GP, including MRSA and VRE
Inhibits RNA polymerase
Forms toxic metabolites in bacterial cell which damage microbial DNA
Hypothesized to bind to cell wall and form channels leading to intracellular K+ depletion
Jaundice
Not to be used as monotherapy (except for prophylaxis)
Known hypersensitivity
Inactivated
by surfactant, therefore not used in MRSA pneumonia Tx