Page 673 - TNFlipTest
P. 673
Toronto Notes 2019 Chest Imaging
Analysis
• tubesandlines:checkpositionandbealertforpneumothoraxorpneumomediastinum • softtissues:neck,axillae,pectoralmuscles,breasts/nipples,chestwall
■ nipple markers can help identify nipples (may mimic lung nodules)
■ amount of soft tissue, presence of masses and air (subcutaneous emphysema) • abdomen(seeAbdominalImaging,MI10)
■ free air under the diaphragm, air-fluid levels, distention in small and large bowels
■ herniation of abdominal contents (i.e. diaphragmatic hernia) • bones:C-spine,thoracicspine,shoulders,ribs,sternum,clavicles
■ lytic and blastic lesions and fractures • mediastinum:trachea,heart,greatvessels
■ cardiomegaly (cardiothoracic ratio >0.5), tracheal shift, tortuous aorta, widened mediastinum • hila:pulmonaryvessels,mainstemandsegmentalbronchi,lymphnodes
• lungs:lungparenchyma,pleura,diaphragm
■ comment on abnormal lung opacity, pleural effusions or thickening
■ right hemidiaphragm usually higher than left due to liver
■ right vs. left hemidiaphragm can be discerned on lateral CXR due to heart resting directly on left
hemidiaphragm
• pleaserefertoTorontoNoteswebsiteforsupplementarymaterialonhowtoapproachaCXR
Anatomy
Localizing Lesions for Parenchymal Lung Disease
• silhouettesign:whentwoobjectsofthesameradiolucencycontacteachother,theybecome indistinguishable on imaging and result in the loss of normal interfaces. It can be used to identify lung pathology (consolidation, atelectasis, mass) and localize disease to specific lung segments. The silhouette sign is not only used in the chest, but can also be an aid to interpreting imaging studies throughout the body
• spinesign:onlateralfilms,vertebralbodiesshouldappearprogressivelyradiolucent(dark)asone moves down the thoracic vertebral column; if they appear more radio-opaque, it is an indication of pathology (e.g. consolidation in overlying left lower lobe)
• airbronchogram:branchingpatternofair-filledbronchionabackgroundofopacification
• airbronchogram:branchingpatternofair-filledbronchionabackgroundoffluid-filledairspaces
Medical Imaging MI5
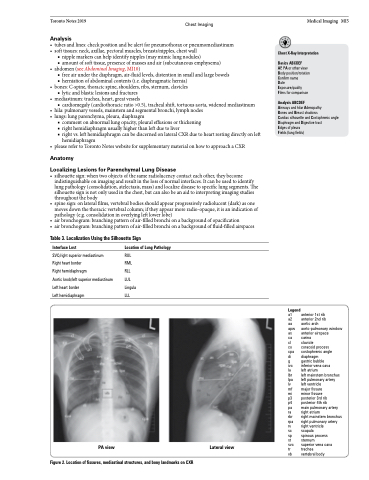
Table 3. Localization Using the Silhouette Sign
Chest X-Ray Interpretation
Basics ABCDEF AP,PAorotherview Body position/rotation Confirm name
Date Exposure/quality Films for comparison
Analysis ABCDEF
Airways and hilar Adenopathy
Bones and Breast shadows
Cardiac silhouette and Costophrenic angle Diaphragm and Digestive tract
Edges of pleura
Fields (lung fields)
Interface Lost
SVC/right superior mediastinum Right heart border
Right hemidiaphragm
Aortic knob/left superior mediastinum Left heart border
Left hemidiaphragm
Location of Lung Pathology
RUL RML RLL LUL Lingula LLL
PA view
Figure 2. Location of fissures, mediastinal structures, and bony landmarks on CXR
Lateral view
Legend
a1 anterior 1st rib
a2 anterior 2nd rib
aa aortic arch
apw aorto-pulmonary window as anterior airspace
ca carina
cl clavicle
co coracoid process
cpa costophrenic angle
di diaphragm
g gastric bubble
ivc inferior vena cava
la left atrium
lbr left mainstem bronchus lpa left pulmonary artery
lv left ventricle
mf major fissure
mi minor fissure
p3 posterior 3rd rib
p4 posterior 4th rib
pa main pulmonary artery ra right atrium
rbr right mainstem bronchus rpa right pulmonary artery
rv right ventricle
sc scapula
sp spinous process
st sternum
svc superior vena cava
tr trachea
vb vertebral body