Page 690 - TNFlipTest
P. 690
MI22 Medical Imaging
Musculoskeletal System Toronto Notes 2019
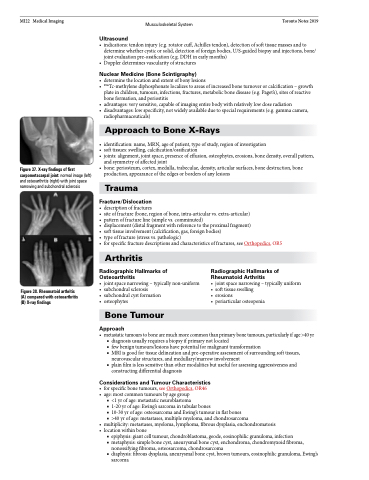
Figure 37. X-ray findings of first carpometacarpal joint: normal image (left) and osteoarthritis (right) with joint space narrowing and subchondral sclerosis
Ultrasound
• indications:tendoninjury(e.g.rotatorcuff,Achillestendon),detectionofsofttissuemassesandto determine whether cystic or solid, detection of foreign bodies, U/S-guided biopsy and injections, bone/ joint evaluation pre-ossification (e.g. DDH in early months)
• Dopplerdeterminesvascularityofstructures
Nuclear Medicine (Bone Scintigraphy)
• determinethelocationandextentofbonylesions
• 99mTc-methylenediphosphonatelocalizestoareasofincreasedboneturnoverorcalcification–growth
plate in children, tumours, infections, fractures, metabolic bone disease (e.g. Paget’s), sites of reactive
bone formation, and periostitis
• advantages:verysensitive,capableofimagingentirebodywithrelativelylowdoseradiation
• disadvantages:lowspecificity,notwidelyavailableduetospecialrequirements(e.g.gammacamera,
radiopharmaceuticals)
Approach to Bone X-Rays
• identification:name,MRN,ageofpatient,typeofstudy,regionofinvestigation
• softtissues:swelling,calcification/ossification
• joints:alignment,jointspace,presenceofeffusion,osteophytes,erosions,bonedensity,overallpattern,
and symmetry of affected joint
• bone:periosteum,cortex,medulla,trabeculae,density,articularsurfaces,bonedestruction,bone
production, appearance of the edges or borders of any lesions
Trauma
Fracture/Dislocation
• descriptionoffractures
• siteoffracture(bone,regionofbone,intra-articularvs.extra-articular)
• patternoffractureline(simplevs.comminuted)
• displacement(distalfragmentwithreferencetotheproximalfragment)
• softtissueinvolvement(calcification,gas,foreignbodies)
• typeoffracture(stressvs.pathologic)
• forspecificfracturedescriptionsandcharacteristicsoffractures,seeOrthopedics,OR5
Figure 38. Rheumatoid arthritis (A) compared with osteoarthritis (B) X-ray findings
Arthritis
Radiographic Hallmarks of Osteoarthritis
• joint space narrowing – typically non-uniform • subchondral sclerosis
• subchondral cyst formation
• osteophytes
Bone Tumour
Approach
Radiographic Hallmarks of Rheumatoid Arthritis
• joint space narrowing – typically uniform • soft tissue swelling
• erosions
• periarticular osteopenia
• metastatictumourstobonearemuchmorecommonthanprimarybonetumours,particularlyifage>40yr ■ diagnosis usually requires a biopsy if primary not located
■ few benign tumours/lesions have potential for malignant transformation
■ MRI is good for tissue delineation and pre-operative assessment of surrounding soft tissues,
neurovascular structures, and medullary/marrow involvement
■ plain film is less sensitive than other modalities but useful for assessing aggressiveness and
constructing differential diagnosis
Considerations and Tumour Characteristics
• forspecificbonetumours,seeOrthopedics,OR46 • age:mostcommontumoursbyagegroup
■ <1 yr of age: metastatic neuroblastoma
■ 1-20 yr of age: Ewing’s sarcoma in tubular bones
■ 10-30 yr of age: osteosarcoma and Ewing’s tumour in flat bones
■ >40 yr of age: metastases, multiple myeloma, and chondrosarcoma
• multiplicity:metastases,myeloma,lymphoma,fibrousdysplasia,enchondromatosis • locationwithinbone
■ epiphysis: giant cell tumour, chondroblastoma, geode, eosinophilic granuloma, infection
■ metaphysis: simple bone cyst, aneurysmal bone cyst, enchondroma, chondromyxoid fibroma,
nonossifying fibroma, osteosarcoma, chondrosarcoma
■ diaphysis: fibrous dysplasia, aneurysmal bone cyst, brown tumours, eosinophilic granuloma, Ewing’s
sarcoma