Page 70 - TNFlipTest
P. 70
C2 Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery
Acronyms
Toronto Notes 2019
Acronyms
AAA abdominal aortic aneurysm
AAA abdominal aortic aneurysm
ABI ankle-brachial index
ACEI angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor ACS acute coronary syndrome
AFib atrial fibrillation
AR aortic regurgitation
ARB angiotensin receptor blocker
ARDS acute respiratory distress syndrome AS aortic stenosis
ASA acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin®)
ASD atrial septal defect
AV atrioventricular
AVM arteriovenous malformation
AVNRT atrioventricular nodal re-entrant
tachycardia
AVRT atrioventricular re-entrant tachycardia BBB bundle brunch block
BNP brain natriuretic peptide
BP blood pressure
BiVAD biventricular assist device
CABG coronary artery bypass graft
CAD coronary artery disease
CCB calcium channel blocker
CHF congestive heart failure
CI cardiac index
CO cardiac output
COPD chronic obstructive pulmonary disease CTA CT angiography
CVD cerebrovascular disease
CXR chest x-ray
DCM dilated cardiomyopathy
DM diabetes mellitus
DOAC direct oral anticoagulant DVT deep vein thrombosis ECASA enteric coated ASA ECG electrocardiogram
Echo echocardiogram
EDP end diastolic pressure
EPS electrophysiology studies
EtOH ethanol/alcohol
GERD gastroesophageal reflux disease HCM hypertrophic cardiomyopathy HFPEF heart failure with preserved
ejection fraction
HFREF heart failure with reduced ejection
fraction
HTN hypertension
HR heart rate
ICD implantable cardioverter-defibrillator IE infective endocarditis
JVP jugular venous pressure
LA left atrium
LAE left atrial enlargement
LBB left bundle branch
LBBB left bundle branch block
LICS left intercostal space
LLSB left lower sternal border
LMWH low molecular weight heparin
LV left ventricle
LVAD left ventricular assist device
LVEF left ventricular ejection fraction LVH left ventricular hypertrophy MAT multifocal atrial tachycardia MI myocardial infarction
MPI myocardial perfusion imaging MR mitral regurgitation
MRA MRI angiography
MS mitral stenosis
NSR normal sinus rhythm
NSTEMI non-ST elevation myocardial infarction NTG nitroglycerin
OS opening snap
PAC premature atrial contraction
PCI percutaneous coronary intervention PCWP pulmonary capillary wedge pressure PDA patent ductus arteriosus
PE pulmonary embolism
PFO patent foramen ovale
PIV posterior-interventricular artery
PMI point of maximal impulse
PND paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
PUD peptic ulcer disease
PVC premature ventricular contraction
PVD peripheral vascular disease
RA right atrium
RAAS renin angiotensin aldosterone system RAE right atrial enlargement
RAO right anterior oblique
RBB right bundle branch
RBBB right bundle branch block
RBW routine blood work
RV right ventricle
RVAD right ventricular assist device
RVH right ventricular hypertrophy
SA sinoatrial
SCD sudden cardiac death
SEM systolic ejection murmur
SLE systemic lupus erythematosus SNS sympathetic nervous system STEMI ST elevation myocardial infarction SV stroke volume
SVC superior vena cava
SVR systemic vascular resistance
SVT supraventricular tachycardia
TAA thoracic aortic aneurysm
TB tuberculosis
TEE transesophageal echocardiography TIA transient ischemic attack
TR tricuspid regurgitation
TTE transthoracic echocardiography UA unstable angina
VAD ventricular assist device
VFib ventricular fibrillation
VT ventricular tachycardia
VTE venous thromboembolism
WPW Wolff-Parkinson-White
Basic Anatomy Review
Coronary Circulation
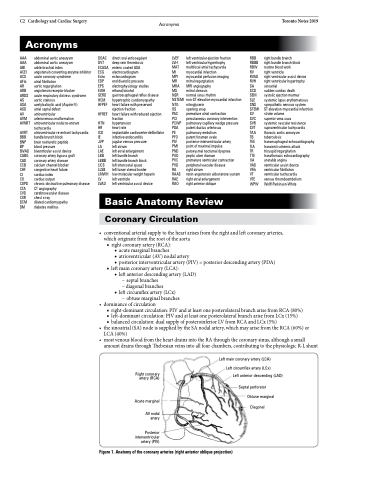
• conventionalarterialsupplytotheheartarisesfromtherightandleftcoronaryarteries, which originate from the root of the aorta
■ right coronary artery (RCA):
◆ acute marginal branches
◆ atrioventricular (AV) nodal artery
◆ posterior interventricular artery (PIV) = posterior descending artery (PDA)
■ left main coronary artery (LCA):
◆ left anterior descending artery (LAD)
– septal branches
– diagonal branches
◆ left circumflex artery (LCx)
– obtuse marginal branches
• dominanceofcirculation
■ right-dominant circulation: PIV and at least one posterolateral branch arise from RCA (80%) ■ left-dominant circulation: PIV and at least one posterolateral branch arise from LCx (15%)
■ balanced circulation: dual supply of posteroinferior LV from RCA and LCx (5%)
• thesinoatrial(SA)nodeissuppliedbytheSAnodalartery,whichmayarisefromtheRCA(60%)or LCA (40%)
• mostvenousbloodfromtheheartdrainsintotheRAthroughthecoronarysinus,althoughasmall amount drains through Thebesian veins into all four chambers, contributing to the physiologic R-L shunt
Right coronary artery (RCA)
Acute marginal
AV nodal artery
Posterior interventricular artery (PIV)
Left main coronary artery (LCA) Left circumflex artery (LCx)
Left anterior descending (LAD)
Septal perforator Obtuse marginal
Diagonal
Figure 1. Anatomy of the coronary arteries (right anterior oblique projection)