Page 703 - TNFlipTest
P. 703
Toronto Notes 2019
Basic Anatomy Review
Nephrology NP3
Table 1. Major Kidney Functions (continued)
Function
4. Blood Pressure Regulation
5. Glucose Homeostasis
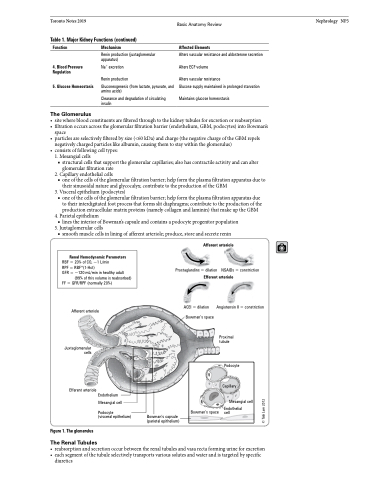
The Glomerulus
Mechanism
Renin production (juxtaglomerular apparatus)
Na+ excretion
Renin production
Gluconeogenesis (from lactate, pyruvate, and amino acids)
Clearance and degradation of circulating insulin
Affected Elements
Alters vascular resistance and aldosterone secretion Alters ECF volume
Alters vascular resistance
Glucose supply maintained in prolonged starvation
Maintains glucose homeostasis
• sitewherebloodconstituentsarefilteredthroughtothekidneytubulesforexcretionorreabsorption
• filtrationoccursacrosstheglomerularfiltrationbarrier(endothelium,GBM,podocytes)intoBowman’s
space
• particlesareselectivelyfilteredbysize(<60kDa)andcharge(thenegativechargeoftheGBMrepels
negatively charged particles like albumin, causing them to stay within the glomerulus)
• consistsoffollowingcelltypes:
1. Mesangial cells
■ structural cells that support the glomerular capillaries; also has contractile activity and can alter
glomerular filtration rate 2. Capillary endothelial cells
■ one of the cells of the glomerular filtration barrier; help form the plasma filtration apparatus due to their sinusoidal nature and glycocalyx; contribute to the production of the GBM
3. Visceral epithelium (podocytes)
■ one of the cells of the glomerular filtration barrier; help form the plasma filtration apparatus due
to their interdigitated foot process that forms slit diaphragms; contribute to the production of the
production extracellular matrix proteins (namely collagen and laminin) that make up the GBM 4. Parietal epithelium
■ lines the interior of Bowman’s capsule and contains a podocyte progenitor population 5. Juxtaglomerular cells
■ smooth muscle cells in lining of afferent arteriole; produce, store and secrete renin
Afferent arteriole
Prostaglandins = dilation NSAIDs = constriction
Renal Hemodynamic Parameters
RBF = 20% of CO, ~1 L/min
RPF = RBF*(1-Hct)
GFR = ~120 mL/min in healthy adult
(99% of this volume is reabsorbed) FF = GFR/RPF (normally 20%)
Efferent arteriole
Afferent arteriole
Juxtaglomerular cells
Efferent arteriole
Endothelium
Angiotensin II = constriction
ACEI = dilation Bowman’s space
Proximal tubule
Mesangial cell
Podocyte
(visceral epithelium)
Bowman’s capsule (parietal epithelium)
Figure 1. The glomerulus
The Renal Tubules
• reabsorptionandsecretionoccurbetweentherenaltubulesandvasarectaformingurineforexcretion • eachsegmentofthetubuleselectivelytransportsvarioussolutesandwaterandistargetedbyspecific
diuretics
Podocyte
Capillary
Mesangial cell
Endothelial Bowman’s space cell
© Tobi Lam 2012