Page 704 - TNFlipTest
P. 704
NP4 Nephrology
Basic Anatomy Review
Toronto Notes 2019
A ACTIVE (requires ATP)
P PARACELLULAR
R REGULATED, hormone
(e.g. angiotensin II, ald, ANF) H2O PERMEABLE segment H2O IMPERMEABLE segment
R ang. II Na+/H+
exchange
H+ Na+
A
Na+/K+ exchange (Na+ 80%)
K+ Na+
R Na+/PO43– co-transport (PTH & vitamin D)
Na+ 10% – K+ – 2Cl- R (ADH) co-transport
Ca2+ – Mg2+ P H2O 2%
Na+/K+ exchang
AQP1
K+ H+
NaCl 5% H2O HCO3– Ca2+
R aldosterone Na+
K+
ENaC channels
R AQP2 by ADH ADH receptor
ADH
AQP channel
H2O
PROXIMAL TUBULE
Osmotic diuretics
DESCENDING THIN LIMB (Loop of Henle)
A
Glucose 90% Amino acids 90% HCO-3 90% H2O 80%
THICK ASCENDING LIMB (Loop of Henle)
Loop diuretics
DISTAL TUBULE
Thiazide diuretics
ASCENDING THIN LIMB (Loop of Henle)
Loop diuretics, synthesizes osmolytes, impermeable to H2O
COLLECTING DUCT
K+ sparing diuretics
NaCl Urea H2O
Glomerular Filtration Rate
GFR = Kf(ΔP–ΔΠ)
Kf = ultrafiltration coefficient
ΔP = hydrostatic pressure difference
between glomerular capillaries and
Bowman’s space
ΔΠ = osmoticpressuredifferencebetween
glomerular capillaries and Bowman’s
space
ΔP – ΔΠ = net outward pressure
e
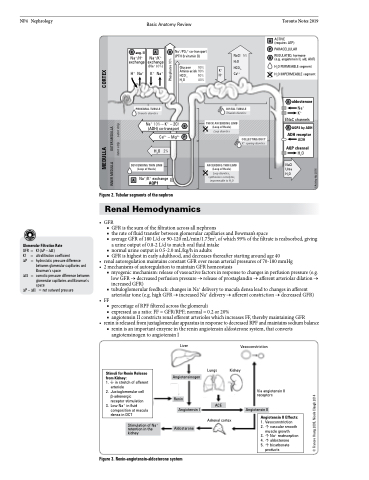
Figure 2. Tubular segments of the nephron
Renal Hemodynamics
• GFR
■ GFR is the sum of the filtration across all nephrons
■ the rate of fluid transfer between glomerular capillaries and Bowman’s space
■ average GFR of 180 L/d or 90-120 mL/min/1.73m2, of which 99% of the filtrate is reabsorbed, giving
a urine output of 0.8-2 L/d to match oral fluid intake
■ normal urine output is 0.5-2.0 mL/kg/h in adults
■ GFR is highest in early adulthood, and decreases thereafter starting around age 40
• renalautoregulationmaintainsconstantGFRovermeanarterialpressuresof70-180mmHg • 2mechanismsofautoregulationtomaintainGFRhomeostasis
■ myogenic mechanism: release of vasoactive factors in response to changes in perfusion pressure (e.g. low GFR → decreased perfusion pressure → release of prostaglandin → afferent arteriolar dilation → increased GFR)
■ tubuloglomerular feedback: changes in Na+ delivery to macula densa lead to changes in afferent arteriolar tone (e.g. high GFR → increased Na+ delivery → afferent constriction → decreased GFR)
• FF■ percentage of RPF filtered across the glomeruli
■ expressed as a ratio: FF = GFR/RPF; normal = 0.2 or 20%
■ angiotensin II constricts renal efferent arterioles which increases FF, thereby maintaining GFR
• reninisreleasedfromjuxtaglomerularapparatusinresponsetodecreasedRPFandmaintainssodiumbalance ■ renin is an important enzyme in the renin angiotensin aldosterone system, that converts
angiotensinogen to angiotensin I
Liver
Angiotensin I
Aldosterone
Vasoconstriction
Stimuli for Renin ReIease from Kidney:
1.in stretch of afferent
arteriole
2. Juxtaglomerular cell
β-adrenergic
receptor stimulation 3. Low Na+ in fluid
composition at macula densa in DCT
Figure 3. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
Angiotensinogen
Renin
Lungs Kid
ACE
Adrenal cortex
ney
Angiotensin II
Via angiotensin II receptors
Angiotensin II Effects:
1. Vasoconstriction
2. vascular smooth
muscle growth 3.Na+ reabsorption 4. aldosterone
5. bicarbonate
Stimulation of Na+ retention in the kidney
products
ADH*
ADH*
© Frances Yeung 2005, Nicole Clough 2014
©Ashley Hui 2016
MEDULLA
CORTEX
INNER MEDULLA OUTER MEDULLA
inner strip outer strip
Phosphates 90%