Page 746 - TNFlipTest
P. 746
N4 Neurology
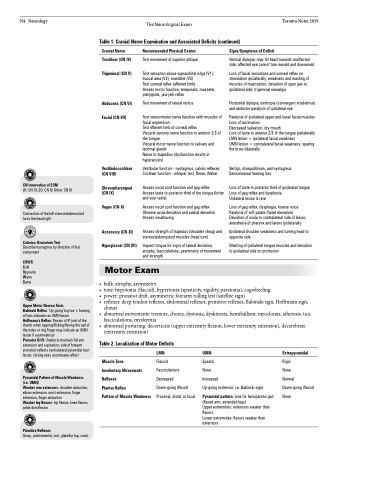
The Neurological Exam Toronto Notes 2019 Table 1. Cranial Nerve Examination and Associated Deficits (continued)
CN Innervation of EOM
LR: CN VI, SO: CN IV, Other: CN III
Contraction of the left sternocleidomastoid turns the head right
Calorics: Brainstem Test
Describe nystagmus by direction of fast component
COWS Cold Opposite Warm Same
Upper Motor Neuron Tests
Babinski Reflex: ‘Up-going‘ big toe ± fanning of toes indicates an UMN lesion
Hoffmann’s Reflex: Flexion of IP joint of the thumb when tapping/flicking/flexing the nail of the index or ring finger may indicate an UMN lesion if asymmetrical
Pronator Drift: Unable to maintain full arm extension and supination; side of forearm pronation reflects contralateral pyramidal tract lesion; closing eyes accentuates effect
Pyramidal Pattern of Muscle Weakness (i.e. UMN)
Weaker arm extensors: shoulder abduction, elbow extension, wrist extension, finger extension, finger abduction
Weaker leg flexors: hip flexion, knee flexion, ankle dorsiflexion
Primitive Reflexes
Grasp, palmomental, root, glabellar tap, snout
Cranial Nerve
Trochlear (CN IV) Trigeminal (CN V)
Abducens (CN VI) Facial (CN VII)
Vestibulocochlear (CN VIII)
Glossopharyngeal (CN IX)
Vagus (CN X)
Accessory (CN XI) Hypoglossal (CN XII)
Recommended Physical Exams
Test movement of superior oblique
Test sensation above supraorbital ridge (V1), buccal area (V2), mandible (V3)
Test corneal reflex (afferent limb)
Assess motor function: temporalis, masseter, pterygoids, jaw jerk reflex
Test movement of lateral rectus
Test sensorimotor nerve function with muscles of facial expression
Test efferent limb of corneal reflex
Visceral sensory nerve function to anterior 2/3 of the tongue
Visceral motor nerve function to salivary and lacrimal glands
Nerve to stapedius (dysfunction results in hyperacusis)
Vestibular function - nystagmus, caloric reflexes Cochlear function - whisper test, Rinne, Weber
Assess vocal cord function and gag reflex
Assess taste to posterior third of the tongue (bitter and sour taste)
Assess vocal cord function and gag reflex Observe uvula deviation and palatal elevation Assess swallowing
Assess strength of trapezius (shoulder shrug) and sternocleidomastoid muscles (head turn)
Inspect tongue for signs of lateral deviation, atrophy, fasciculations, asymmetry of movement and strength
Signs/Symptoms of Deficit
Vertical diplopia; may tilt head towards unaffected side; affected eye cannot turn inward and downward
Loss of facial sensations and corneal reflex on stimulation ipsilaterally, weakness and wasting of muscles of mastication, deviation of open jaw to ipsilateral side; trigeminal neuralgia
Horizontal diplopia, esotropia (convergent strabismus) and abductor paralysis of ipsilateral eye
Paralysis of ipsilateral upper and lower facial muscles Loss of lacrimation
Decreased salivation, dry mouth
Loss of taste to anterior 2/3 of the tongue ipsilaterally LMN lesion = ipsilateral facial weakness
UMN lesion = contralateral facial weakness, sparing the brow bilaterally
Vertigo, disequilibrium, and nystagmus Sensorineural hearing loss
Loss of taste in posterior third of ipsilateral tongue Loss of gag reflex and dysphasia
Unilateral lesion is rare
Loss of gag reflex, dysphagia, hoarse voice Paralysis of soft palate (failed elevation) Deviation of uvula to contralateral side of lesion; anesthesia of pharynx and larynx ipsilaterally
Ipsilateral shoulder weakness and turning head to opposite side
Wasting of ipsilateral tongue muscles and deviation to ipsilateral side on protrusion
Motor Exam
• bulk: atrophy, asymmetry
• tone:hypotonia(flaccid),hypertonia(spasticity,rigidity,paratonia),cogwheeling
• power:pronatordrift,asymmetricforearmrollingtest(satellitesign)
• reflexes:deeptendonreflexes,abdominalreflexes,primitivereflexes,Babinskisign,Hoffmannsign,
clonus
• abnormal movements: tremors, chorea, dystonia, dyskinesia, hemiballism, myoclonus, athetosis, tics,
fasciculations, myokymia
• abnormal posturing: decorticate (upper extremity flexion, lower extremity extension), decerebrate
(extremity extension)
Table 2. Localization of Motor Deficits
Muscle Tone
Involuntary Movements Reflexes
Plantar Reflex
Pattern of Muscle Weakness
LMN
Flaccid
Fasciculations Decreased
Down-going (flexor) Proximal, distal, or focal
UMN
Spastic
None
Increased
Up-going (extensor, i.e. Babinski sign)
Pyramidal pattern: look for hemiparetic gait (flexed arm, extended legs)
Upper extremities: extensors weaker than flexors
Lower extremities: flexors weaker than extensors
Extrapyramidal
Rigid
None
Normal Down-going (flexor) None