Page 747 - TNFlipTest
P. 747
Toronto Notes 2019
The Neurological Exam
Neurology N5
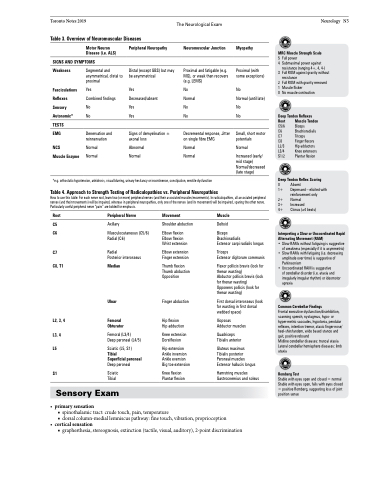
Table 3. Overview of Neuromuscular Diseases
Motor Neuron Disease (i.e. ALS)
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
Peripheral Neuropathy
Distal (except GBS) but may be asymmetrical
Yes Decreased/absent Yes
Yes
Signs of demyelination ± axonal loss
Abnormal Normal
Neuromuscular Junction
Proximal and fatigable (e.g. MG), or weak then recovers (e.g. LEMS)
No Normal No
No
Decremental response, Jitter on single fibre EMG
Normal Normal
Myopathy
Proximal (with some exceptions)
No
Normal (until late) No
No
Small, short motor potentials
Normal
Increased (early/ mid stage) Normal/decreased (late stage)
MRC Muscle Strength Scale
5 Fullpower
4 Submaximalpoweragainst
resistance (ranging 4+, 4, 4-)
3 FullROMagainstgravitywithout
resistance
2 FullROMwithgravityremoved 1 Muscleflicker
0 Nomusclecontraction
Deep Tendon Reflexes Root Muscle Tendon C5/6 Biceps
C6 Brachioradialis C7 Triceps
C8 Finger flexors L2/3 Hip adductors L3/4 Knee extensors S1/2 Plantar flexion
Deep Tendon Reflex Scoring
0 Absent
1+ Depressed – elicited with
reinforcement only
2+ Normal
3+ Increased
4+ Clonus (≥4 beats)
Interpreting a Slow or Uncoordinated Rapid Alternating Movement (RAM)
• Slow RAMs without fatiguing is suggestive
of weakness (especially if it is asymmetric) • Slow RAMs with fatiguing (i.e. decreasing
amplitude over time) is suggestive of
Parkinsonism
• Uncoordinated RAM is suggestive
of cerebellar disorder (i.e. ataxia and irregularly irregular rhythm) or ideomotor apraxia
Common Cerebellar Findings
Frontal executive dysfunction/disinhibition, scanning speech, nystagmus, hypo- or hyper-metric saccades, hypotonia, pendular reflexes, intention tremor, ataxic finger-nose/ heel-shin/tandem, wide based stance and gait, positive rebound
Midline cerebellar diseases: truncal ataxia Lateral cerebellar hemisphere diseases: limb ataxia
Romberg Test
Stable with eyes open and closed = normal Stable with eyes open, falls with eyes closed = positive Romberg, suggesting loss of joint position sense
Weakness
Fasciculations Reflexes Sensory Autonomic*
TESTS
EMG
NCS
Muscle Enzyme
Segmental and asymmetrical, distal to proximal
Yes
Combined findings No
No
Denervation and reinnervation
Normal Normal
*e.g. orthostatic hypotension, anhidrosis, visual blurring, urinary hesitancy or incontinence, constipation, erectile dysfunction
Table 4. Approach to Strength Testing of Radiculopathies vs. Peripheral Neuropathies
How to use this table: For each nerve root, learn two (or more) peripheral nerves (and their associated muscles/movements). In radiculopathies, all associated peripheral nerves (and their movements) will be impaired, whereas in peripheral neuropathies, only one of the nerves (and its movement) will be impaired, sparing the other nerve. Particularly useful peripheral nerve “pairs” are bolded for emphasis.
Root
C5 C6
C7 C8, T1
L2, 3, 4 L3, 4 L5
S1
Peripheral Nerve
Axillary
Musculocutaneous (C5/6) Radial (C6)
Radial
Posterior interosseus
Median
Ulnar
Femoral Obturator
Femoral (L3/4)
Deep peroneal (L4/5)
Sciatic (L5, S1)
Tibial
Superficial peroneal Deep peroneal
Sciatic Tibial
Movement
Shoulder abduction
Elbow flexion Elbow flexion Wrist extension
Elbow extension Finger extension
Thumb flexion Thumb abduction Opposition
Finger abduction
Hip flexion Hip adduction
Knee extension Dorsiflexion
Hip extension Ankle inversion Ankle eversion Big toe extension
Knee flexion Plantar flexion
Muscle
Deltoid
Biceps
Brachioradialis
Extensor carpi radialis longus
Triceps
Extensor digitorum communis
Flexor pollicis brevis (look for thenar wasting)
Abductor pollicis brevis (look for thenar wasting) Opponens pollicis (look for thenar wasting)
First dorsal interosseus (look for wasting in first dorsal webbed space)
Iliopsoas Adductor muscles
Quadriceps Tibialis anterior
Gluteus maximus Tibialis posterior Peroneal muscles Extensor hallucis longus
Hamstring muscles Gastrocnemius and soleus
Sensory Exam
• primarysensation
■ spinothalamic tract: crude touch, pain, temperature
■ dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway: fine touch, vibration, proprioception
• corticalsensation
■ graphesthesia, stereognosis, extinction (tactile, visual, auditory), 2-point discrimination