Page 85 - TNFlipTest
P. 85
Toronto Notes 2019 Arrhythmias Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery C17
2. Delayed Afterdepolarizations
■ occur after the action potential has fully repolarized, but before the next usual action potential, thus called a delayed afterdepolarization
■ commonly occurs in situations of high intracellular calcium (e.g. digitalis intoxication, ischemia) or during enhanced catecholamine stimulation (e.g. “twitchy” pacemaker cells)
Alterations in Impulse Conduction
A. Re-Entry Circuits
■ the presence of self-sustaining re-entry circuit causes rapid repeated depolarizations in a region of myocardium (see Figure 26, C20, for an example in the context of AV nodal re-entrant tachycardia)
◆ e.g. myocardium that is infarcted/ischemic will consist of non-excitable and partially excitable zones which will promote the formation of re-entry circuits
B. Conduction Block
■ ischemia, fibrosis, trauma, and drugs can cause transient, permanent, unidirectional or bidirectional block
■ most common cause of block is due to refractory myocardium (cardiomyocytes are in refractory period or zone of myocardium unexcitable due to fibrosis)
■ if block occurs along the specialized conduction system distal zones of the conduction system can assume pacemaking control
■ conduction block can lead to bradycardia or tachycardia when impaired conduction leads to re- entry phenomenon
C. Bypass Tracts
■ normally the only conducting tract from the atria to the ventricles is the AV node into the His- Purkinje system
■ congenital/acquired accessory conducting tracts bypass the AV node and facilitate premature ventricular activation before normal AV node conduction
■ see Pre-Excitation Syndromes, C21
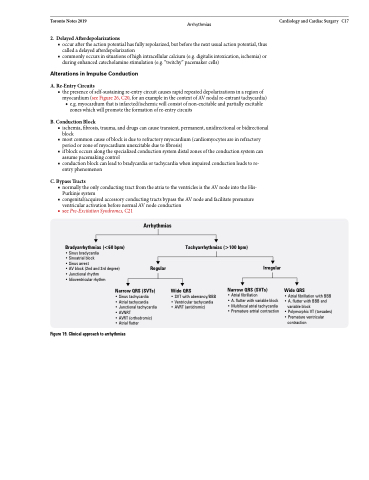
Bradyarrhythmias (<60 bpm)
• Sinus bradycardia
• Sinoatrial block
• Sinus arrest
• AV block (2nd and 3rd degree) • Junctional rhythm
• Idioventricular rhythm
Arrhythmias
Regular
Tachyarrhythmias (>100 bpm)
Figure 19. Clinical approach to arrhythmias
Narrow QRS (SVTs)
• Sinus tachycardia
• Atrial tachycardia
• Junctional tachycardia • AVNRT
• AVRT (orthodromic)
• Atrial flutter
Wide QRS
• SVT with aberrancy/BBB • Ventricular tachycardia • AVRT (antidromic)
Irregular
Narrow QRS (SVTs)
• Atrial fibrillation
• A. flutter with variable block • Multifocal atrial tachycardia • Premature artrial contraction
Wide QRS
• Atrial fibrillation with BBB • A. flutter with BBB and
variable block
• Polymorphic VT (torsades) • Premature ventricular
contraction