Page 910 - TNFlipTest
P. 910
OP20 Ophthalmology Lens Lens
• consistsofanoutercapsulesurroundingasoftcortexandafirminnernucleus
Cataracts
• anyopacityofthelens,regardlessofetiology
• mostcommoncauseofreversibleblindnessworldwide
• types:nuclearsclerosis,cortical,andposteriorsubcapsular
Etiology
• acquired
subcapsular ■ age-related (over 90% of all cataracts)
Toronto Notes 2019
Nuclear sclerosis
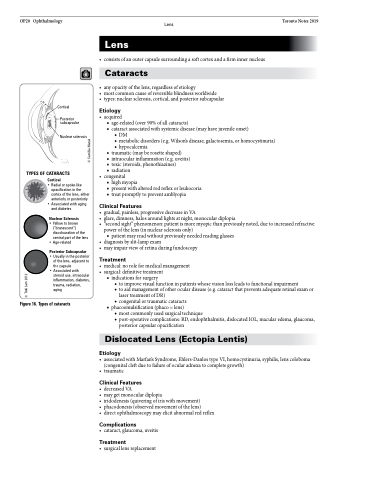
TYPES OF CATARACTS
Cortical
■ cataract associated with systemic disease (may have juvenile onset) ◆ DM
◆ metabolic disorders (e.g. Wilson’s disease, galactosemia, or homocystinuria)
◆ hypocalcemia
■ traumatic (may be rosette shaped)
■ intraocular inflammation (e.g. uveitis) ■ toxic (steroids, phenothiazines)
■ radiation
• congenital
■ high myopia
■ present with altered red reflex or leukocoria
Cortical Posterior
• Radial or spoke-like
opacification in the
cortex of the lens, either ■ treat promptly to prevent amblyopia anteriorly or posteriorly
• Associated with aging and diabetes
Nuclear Sclerosis
• Yellow to brown (“brunescent”) discolouration of the central part of the lens
• Age-related
Clinical Features
P
• gradual,painless,progressivedecreaseinVA
• glare, dimness, halos around lights at night, monocular diplopia
• “secondsight”phenomenon:patientismoremyopicthanpreviouslynoted,duetoincreasedrefractive
power of the lens (in nuclear sclerosis only)
■ patient may read without previously needed reading glasses
• diagnosis by slit-lamp exam
• mayimpairviewofretinaduringfundoscopy
Treatment
• medical:noroleformedicalmanagement • surgical:definitivetreatment
■ indications for surgery
◆ to improve visual function in patients whose vision loss leads to functional impairment
◆ to aid management of other ocular disease (e.g. cataract that prevents adequate retinal exam or
laser treatment of DR)
◆ congenital or traumatic cataracts
■ phacoemulsification(phaco=lens)
◆ most commonly used surgical technique
◆ post-operative complications: RD, endophthalmitis, dislocated IOL, macular edema, glaucoma,
posterior capsular opacification
Dislocated Lens (Ectopia Lentis)
Etiology
• associatedwithMarfan’sSyndrome,Ehlers-DanlostypeVI,homocystinuria,syphilis,lenscoloboma (congenital cleft due to failure of ocular adnexa to complete growth)
• traumatic
Clinical Features
• decreasedVA
• maygetmonoculardiplopia
• iridodenesis(quiveringofiriswithmovement)
• phacodonesis(observedmovementofthelens)
• directophthalmoscopymayelicitabnormalredreflex
Complications
• cataract, glaucoma, uveitis
Treatment
• surgicallensreplacement
P
erior Subcapsular
• •
t
o
o
s
s
t
e
U
U
ually in the posterior
o
t
f
s
u
s
o
t
the lens, adjacent to
f
• •
h
t
e capsule
h
e
A
A
sociated with
s
s
s
s
s
eroid use, intraocular
i
lammation, diabetes,
t
f
t
n
e
i
t
n
f
l
t
uma, radiation,
r
r
a
a
u
ag
Figure 16. Types of cataracts
i
ing
© Camillia Matuk
© Tobi Lam 2012