Page 1288 - TNFlipTest
P. 1288
RH2 Rheumatology
Acronyms
Toronto Notes 2019
Acronyms
Ab antibody
ACPA anti-citrullinated protein antibodies Ag antigen
ANA antinuclear antibody
ANCA antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody Anti-RNP antiribonuclear protein
Anti-Sm anti-Smithantibodies
APLA antiphospholipid antibody syndrome AS ankylosing spondylitis
AVN avascular necrosis
BUN blood urea nitrogen
CBC complete blood count
CCB calcium channel blocker
CCP cyclic citrullinated peptide
CMC carpometacarpal joint
CNS central nervous system
CTD connective tissue disease
CPPD calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate CRP C-reactive protein
DEXA dual energy X-ray absorptiometry
Terminology in Rheumatology
Arthritis
• Joint swelling: effusion/synovial thickening • Decreased ROM
• Stress pain (pain at the end of ROM)
• Increased warmth
Arthralgia: perception of joint pain without obvious clinical findings
Active Joint: swollen joint, joint line tenderness, or stress pain
Innate Immune Cells
• Neutrophil (PMN): circulate in blood and
respond to inflammatory stimuli, kill invading organisms by phagocytosis, degranulation, and neutrophil extracellular traps
• Natural Killer Cell: innate immunity against intracellular infections (especially viruses), killing function, and produce cytokines
• Macrophage: arrive after PMNs, suppress PMN efflux and phagocytose PMN debris, secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines in response to microbial debris
• Dendritic Cell: actively phagocytic when immature, activated by signals from toll-like receptor (TLR), release pro-inflammatory cytokines, present antigens to T cells in lymph nodes
• Eosinophil: respond to inflammatory cytokines and degranulate, releasing reactive oxygen species, and cytokines, associated with allergy, asthma and parasitic infection
• Mast Cell: present in connective tissue and mucosa, allergen cross-linking of IgE bound to mast cell triggers degranulation and release of inflammatory mediators
Key Cytokine Targets of Biologic Drugs TNF
• Source: T cells, macrophages
• Major Functions: cachexia, induces other
cytokines, T cell stimulation, induces metalloproteinases and prostaglandins, increases expression of adhesion molecules; increases vascular permeability leading to increased entry of IgG, complement and cells into tissues
IL-6
• Source: Many cells
• Major Functions: proliferation of B and T
cells, acute phase reactant, induces natural protease inhibitor
DIP distal interphalangeal joint DM diabetes mellitus
DMARD disease-modifying
anti-rheumatic drug DMM dermatomyositis
dsDNA double stranded DNA
EA enteropathic arthritis
ECASA enteric-coated acetylsalicylic
acid
ESR erythrocyte sedimentation rate
GC Neisseria gonorrhoeae gonococcus GCA giant cell arteritis
GPA granulomatosis with polyangiitis H/A headache
Hb hemoglobin
HLA human leukocyte antigen
IA intra-articular
IBD inflammatory bowel disease
ILD interstitial lung disease
ITP idiopathic thrombocytopenic
purpura
MCP metacarpalphalangeal joint
MCTD mixed connective tissue disease MHC major histocompatibility complex MPO myeloperoxidase
MTP metatarsal phalangeal joint
MTX methotrexate
OA osteoarthritis
PAN polyarteritis nodosa
PIP proximal interphalangeal joint PM polymyositis
PMN polymorphonuclear leukocyte PMR polymyalgia rheumatica
PsA psoriatic arthritis
PTT partial thromboplastin time PUD peptic ulcer disease
RA rheumatoid arthritis
RBC red blood cell
ReA reactive arthritis
RF rheumatoid factor
ROM range of motion
SI sacroiliac
SLE systemic lupus erythematosus SNRI serotonin-norepinephrine
reuptake inhibitors SS Sjögren’s syndrome
SSA Sjögren’s syndrome antigen A SSB Sjögren’s syndrome antigen B TNF tumour necrosis factor
U/A urinalysis
ULN upper limit of normal U-SpA undifferentiated
spondyloarthropathy VDRL venereal disease research
laboratory WBC white blood cell
Synovitis Effusion
Joint space narrowing
Inflammatory Joint
IE
infective endocarditis
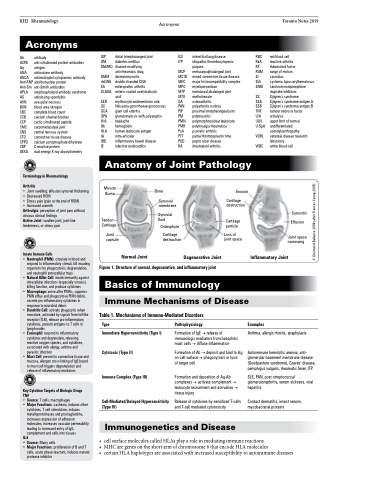
Anatomy of Joint Pathology
Muscle Bursa
Bone
Synovial membrane
Synovial fluid
Osteophyte
Cartilage destruction
Erosion
Cartilage destruction
Cartilage particle
Loss of joint space
Tendon Cartilage
Joint capsule
Normal Joint
Degenerative Joint
Figure 1. Structure of normal, degenerative, and inflammatory joint
Basics of Immunology
Immune Mechanisms of Disease
Table 1. Mechanisms of Immune-Mediated Disorders
Type
Immediate Hypersensitivity (Type I) Cytotoxic (Type II)
Immune Complex (Type III)
Cell-Mediated/Delayed Hypersensitivity (Type IV)
Pathophysiology
Formation of IgE → release of immunologic mediators from basophils/ mast cells → diffuse inflammation
Formation of Ab → deposit and bind to Ag on cell surface → phagocytosis or lysis
of target cell
Formation and deposition of Ag-Ab complexes → activate complement → leukocyte recruitment and activation → tissue injury
Release of cytokines by sensitized T-cells and T-cell mediated cytotoxicity
Examples
Asthma, allergic rhinitis, anaphylaxis
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia, anti- glomerular basement membrane disease (Goodpasture syndrome), Graves’ disease, pemphigus vulgaris, rheumatic fever, ITP
SLE, PAN, post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis, serum sickness, viral hepatitis
Contact dermatitis, insect venom, mycobacterial proteins
Immunogenetics and Disease
• cellsurfacemoleculescalledHLAsplayaroleinmediatingimmunereactions
• MHC are genes on the short arm of chromosome 6 that encode HLA molecules
• certainHLAhaplotypesareassociatedwithincreasedsusceptibilitytoautoimmunediseases
© Desmond Ballance 2006 (after Frances Yeung 2005)