Page 77 - TNFlipTest
P. 77
Toronto Notes 2019
Approach to ECGs
Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery C9
Drug Effects
• digitalis–rarein2018;<1/1000cardiacpatientsoverall
■ therapeutic levels may be associated with “digitalis effect”
◆ ST downsloping or “scooping”
◆ T wave depression or inversion
◆ QT shortening ± U waves
◆ slowing of ventricular rate in AFib ◆ toxic levels associated with:
– arrhythmias: paroxysmal atrial tachycardia (PAT) with conduction block, severe bradycardia in AFib, accelerated junctional rhythms, PVCs, ventricular tachycardia (see Arrhythmias, C16)
– “regularization” of ventricular rate in AFib due to a junctional rhythm and AV dissociation • amiodarone,quinidine,phenothiazines,tricyclicantidepressants,antipsychotics,someantihistamines,
and some antibiotics (prolonged QT interval, U waves)
Figure 14. Atrial fibrillation, ST change due to digitalis (“digitalis effect”)
Pulmonary Disorders
• corpulmonale(oftensecondarytoCOPD)
■ low voltage, right axis deviation (RAD), poor R wave progression in precordial leads ■ RAEandRVHwithstrain
■ multifocal atrial tachycardia (MAT)
• massivepulmonaryembolism(PE)
■ sinus tachycardia and AFib/atrial flutter are the most common arrhythmias
■ RAD, RVH with strain
■ most specific sign is S1Q3T3 (S in I, Q and inverted T wave in III) but rather uncommon
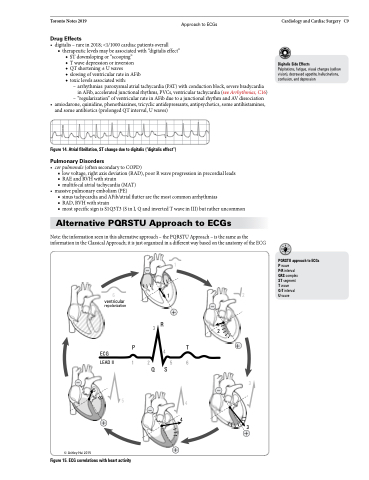
Alternative PQRSTU Approach to ECGs
Note: the information seen in this alternative approach – the PQRSTU Approach – is the same as the information in the Classical Approach; it is just organized in a different way based on the anatomy of the ECG
Digitalis Side Effects
Palpitations, fatigue, visual changes (yellow vision), decreased appetite, hallucinations, confusion, and depression
1
6 1 2
PQRSTU approach to ECGs Pwave
P-R interval
QRS complex
ST segment T wave
Q-T interval Uwave
–
ventricular
–
2
+
repolarization
+
3R P4T
1256
QS
ECG LEAD II
–3 5–
5
+
–
4
4
3
+
© Ashley Hui 2015
+
Figure 15. ECG correlations with heart activity