Page 685 - TNFlipTest
P. 685
Toronto Notes 2019 Genitourinary System and Adrenal
Retrograde Pyelography
• indications:visualizetheurinarycollectingsystemviaacystoscope,ureteralcatheterization,and retrograde injection of contrast medium, visualized by radiograph or fluoroscopy; ordered when the intrarenal collecting system and ureters cannot be opacified using intravenous techniques (patient with impaired renal function, high grade obstruction or allergy to IV contrast)
• findings:onlyyieldsinformationaboutthecollectingsystems(renalpelvisandassociatedstructures), no information regarding the parenchyma of the kidney
Voiding Cystourethrogram
• bladderfilledwithcontrasttothepointwherevoidingistriggered
• fluoroscopy(continuous,real-time)tovisualizebladderduringvoiding
• indications:malesoryoungfemaleswithrecurrentUTIs,hydronephrosis,hydroureter,suspectedlower
urinary tract obstruction, suspected bladder trauma or vesicoureteral reflux • findings:contractilityandevidenceofvesicoureteralreflux
Retrograde Urethrogram
• asmallFoleycatheterplacedintopenileurethralopening,followedbyinstillationofcontrastand radiographic imaging
• indications:usedmainlytostudystricturesortraumatothemaleurethra;first-linestudyiftraumawith blood present at urethral meatus, scrotal hematoma present or high-riding prostate (signs of urethral injury)
MRI
• advantages:bettercontrastresolutionandtissuediscrimination,lackofexposuretoionizingradiation, safer contrast, ability to obtain imaging directly from multiple planes (coronal, sagittal, oblique)
• indications:indicatedoverCTfordepictionofrenalmassesinpatientswithpreviousnephron-sparing surgery, patients requiring serial follow-up (less radiation dosage), patients with reduced renal function, patients with solitary kidneys, clinical staging of prostate cancer (endorectal coil MRI)
Medical Imaging MI17
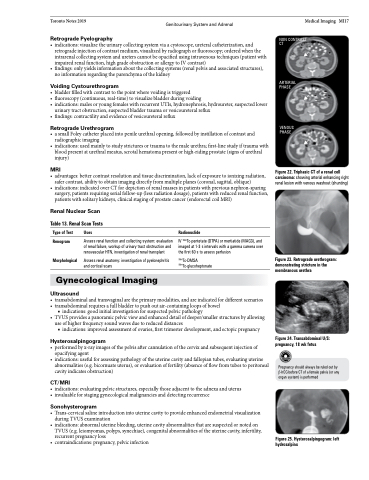
NON CONTRAST CT
ARTERIAL PHASE
VENOUS PHASE
Renal Nuclear Scan
Table 13. Renal Scan Tests
Figure 22. Triphasic CT of a renal cell carcinoma: showing arterial enhancing right renal lesion with venous washout (shunting)
Figure 23. Retrograde urethrogram: demonstrating stricture in the membranous urethra
Figure 24. Transabdominal U/S: pregnancy, 18 wk fetus
Pregnancy should always be ruled out by β-hCG before CT of a female pelvis (or any organ system) is performed
Figure 25. Hysterosalpingogram: left hydrosalpinx
Type of Test
Renogram Morphological
Uses
Assess renal function and collecting system: evaluation of renal failure, workup of urinary tract obstruction and renovascular HTN, investigation of renal transplant
Assess renal anatomy: investigation of pyelonephritis and cortical scars
Radionuclide
IV 99mTc-pentetate (DTPA) or mertiatide (MAG3), and imaged at 1-3 s intervals with a gamma camera over the first 60 s to assess perfusion
99mTc-DMSA 99mTc-glucoheptonate
Gynecological Imaging
Ultrasound
• transabdominalandtransvaginalaretheprimarymodalities,andareindicatedfordifferentscenarios
• transabdominalrequiresafullbladdertopushoutair-containingloopsofbowel
■ indications: good initial investigation for suspected pelvic pathology
• TVUSprovidesapanoramicpelvicviewandenhanceddetailofdeeper/smallerstructuresbyallowing
use of higher frequency sound waves due to reduced distances
■ indications: improved assessment of ovaries, first trimester development, and ectopic pregnancy
Hysterosalpingogram
• performedbyx-rayimagesofthepelvisaftercannulationofthecervixandsubsequentinjectionof opacifying agent
• indications:usefulforassessingpathologyoftheuterinecavityandfallopiantubes,evaluatinguterine abnormalities (e.g. bicornuate uterus), or evaluation of fertility (absence of flow from tubes to peritoneal cavity indicates obstruction)
CT/MRI
• indications:evaluatingpelvicstructures,especiallythoseadjacenttotheadnexaanduterus • invaluableforstaginggynecologicalmalignanciesanddetectingrecurrence
Sonohysterogram
• Trans-cervicalsalineintroductionintouterinecavitytoprovideenhancedendometrialvisualization during TVUS examination
• indications:abnormaluterinebleeding,uterinecavityabnormalitiesthataresuspectedornotedon TVUS (e.g. leiomyomas, polyps, synechiae), congenital abnormalities of the uterine cavity, infertility, recurrent pregnancy loss
• contraindications:pregnancy,pelvicinfection